Sometimes you need to pass data to your application. E.g: API key, credentials, debug parameters. For this reason, Qovery allows you to securely pass your data by using Environment Variables.
Here is a short video to show how to use environment variables.
Tutorial
Here is an example on how to pass an environment variable to a NodeJS app.
Let's first create a new Node.js application that uses environment variables.
Create an environment variable
Let's say that we pass an environment variable
ENABLE_DEBUGthat turns on the debug info from the app.Click on the
environment variablestab inside your app view.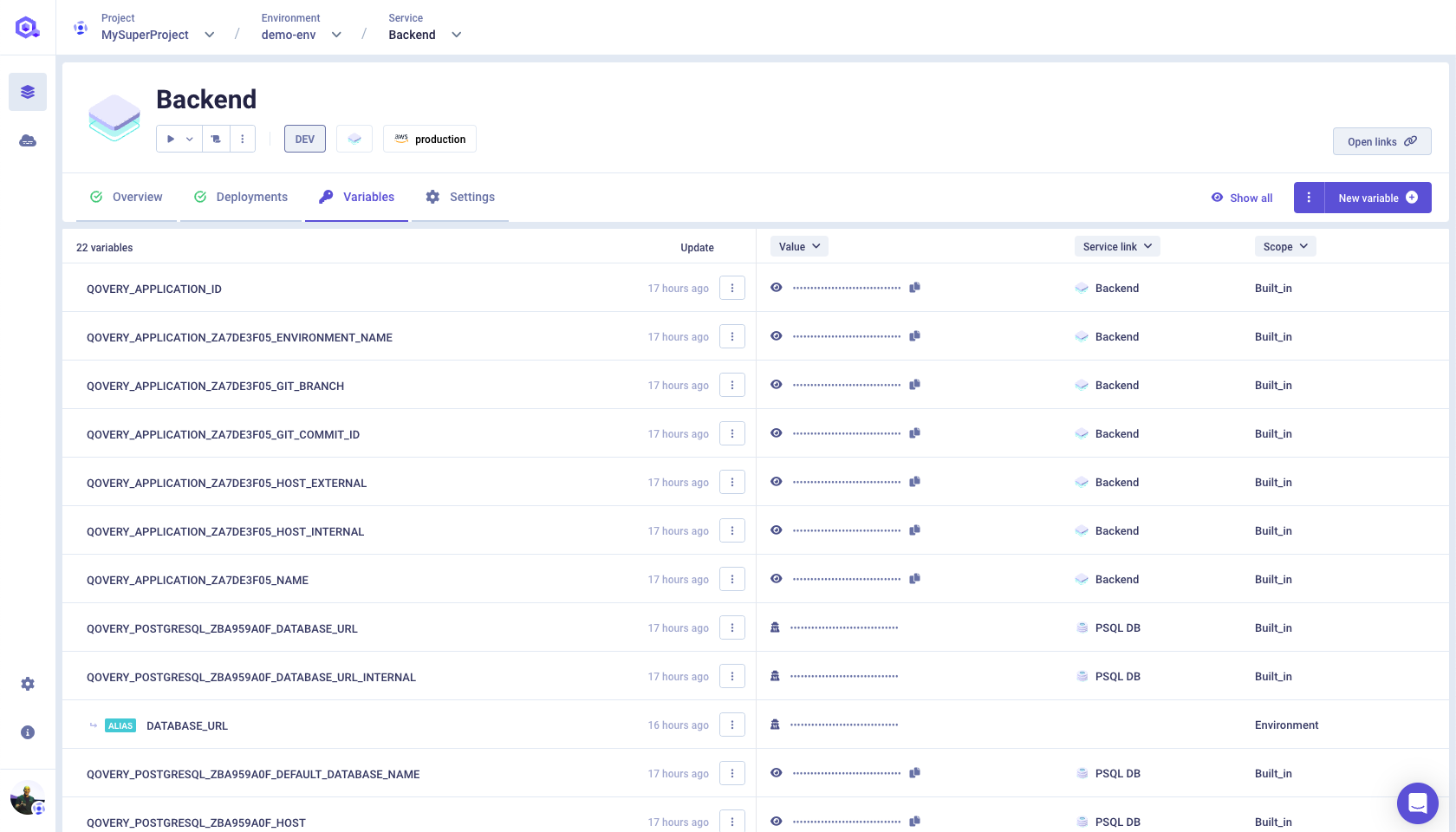
Click on "create", and then add the
ENABLE_DEBUGvariable with a boolean value.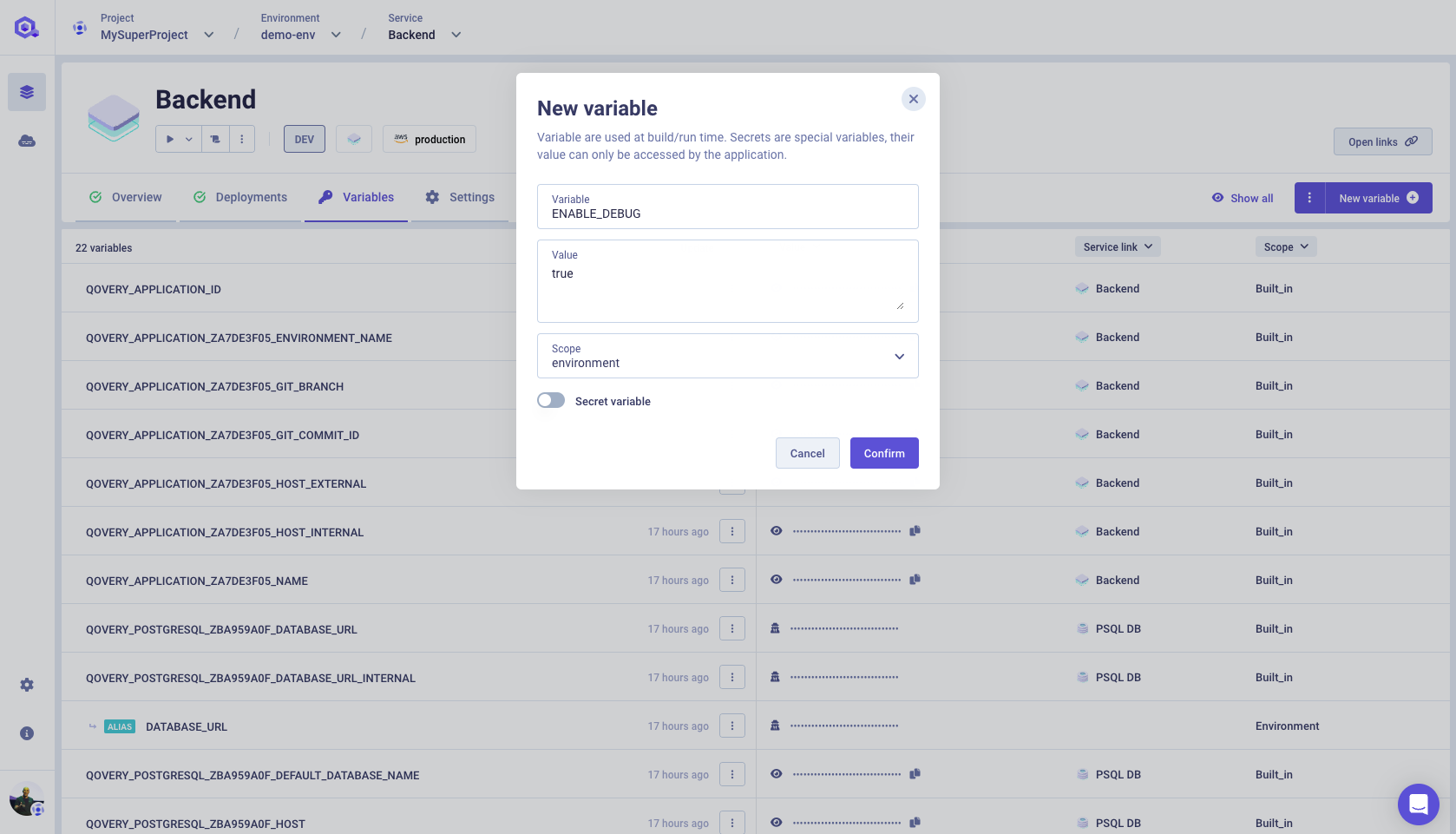
Use the environment variable in the app
Create
app.jsfile - a simple Node.js HTTP server application:app.jsconst http = require('http');const hostname = '0.0.0.0';const port = 3333;const enableDebug = process.env.ENABLE_DEBUGif (enableDebug) {console.log("debug mode enabled");}const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {res.statusCode = 200;res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain');res.end("hello world");});server.listen(port, hostname, () => {console.log(`Server running at http://${hostname}:${port}/`);});As you can see, to get access to your environment variable you just need to use process.env.
ENABLE_DEBUG. Environment variables are injected at the build and run time.
This guide was an introduction on how to use the Environment Variables. To know more about Environment Variables and Secrets, go to our detailed documentation.