Message queuing service enables you to decouple and scale microservices, distributed systems, and serverless applications. In this guide, we'll show you how to leverage a queue system (Amazon SQS) to build a highly scalable backend.
Using Amazon SQS eliminates the complexity and overhead associated with managing and operating message-oriented middleware and empowers developers to focus on differentiating work. With SQS, you can send, store, and receive messages between software components at any volume without losing messages or requiring other services to be available.
Goal
In this guide, we'll create a backend microservice that sends messages on an event queue. Additionally, we'll go through two ways of consuming and processing those messages:
- We will use
AWS Lambdato process events from the queue in a serverless way - We will use Qovery-managed backend application workers to process events from the queue
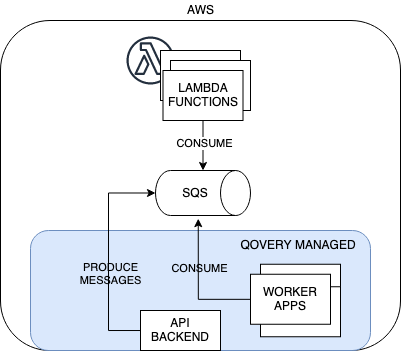
As for now, Qovery does not natively integrate with AWS Lambda and SQS, but the integration part is quite easy, and we will go through it in the following steps.
The backend application and workers servers that consume messages from the queue will be fully managed and deployed by Qovery.
Let's get started.
Configure SQS
Open Amazon SQS service in AWS Console and click on Create Queue
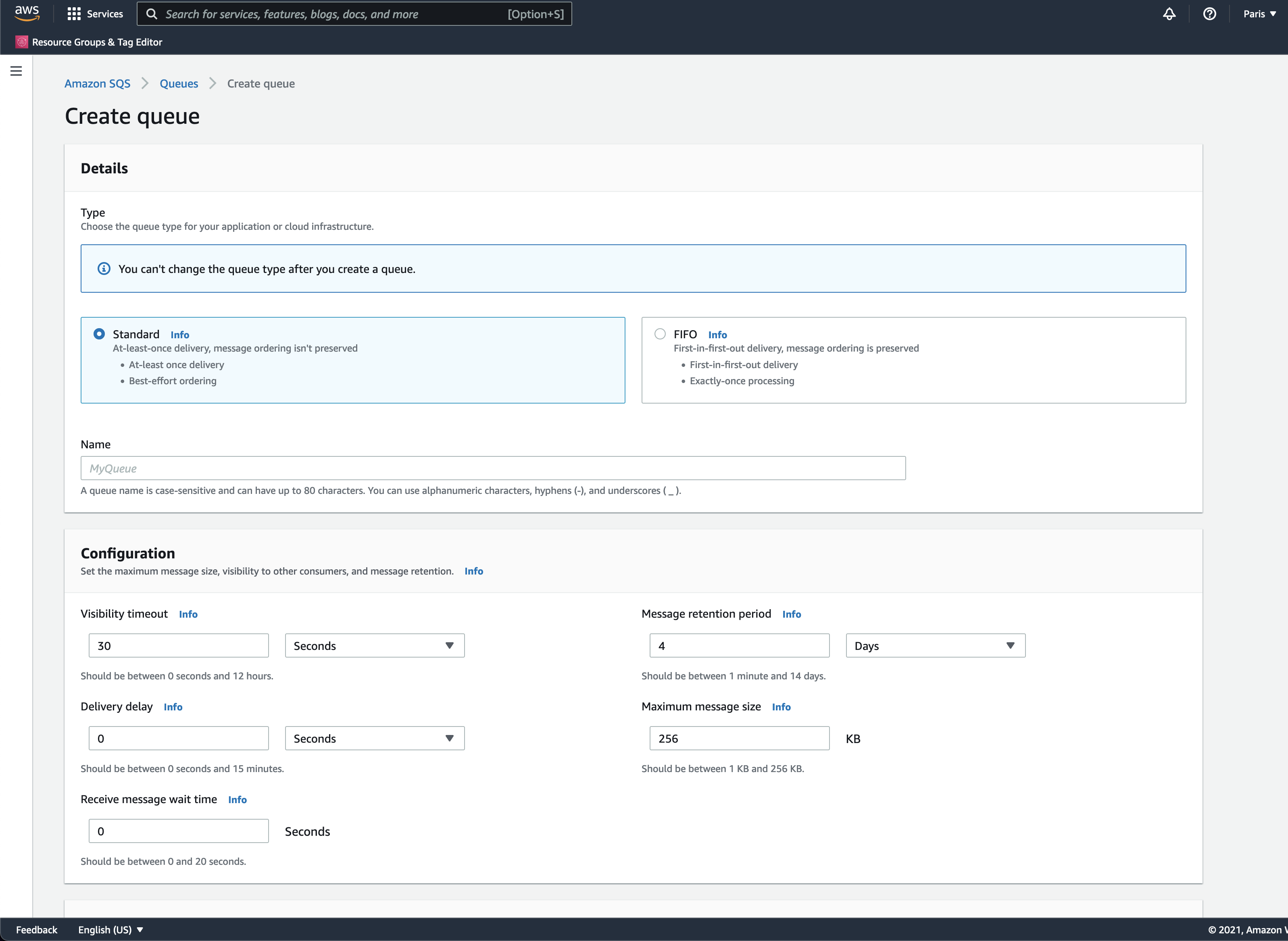
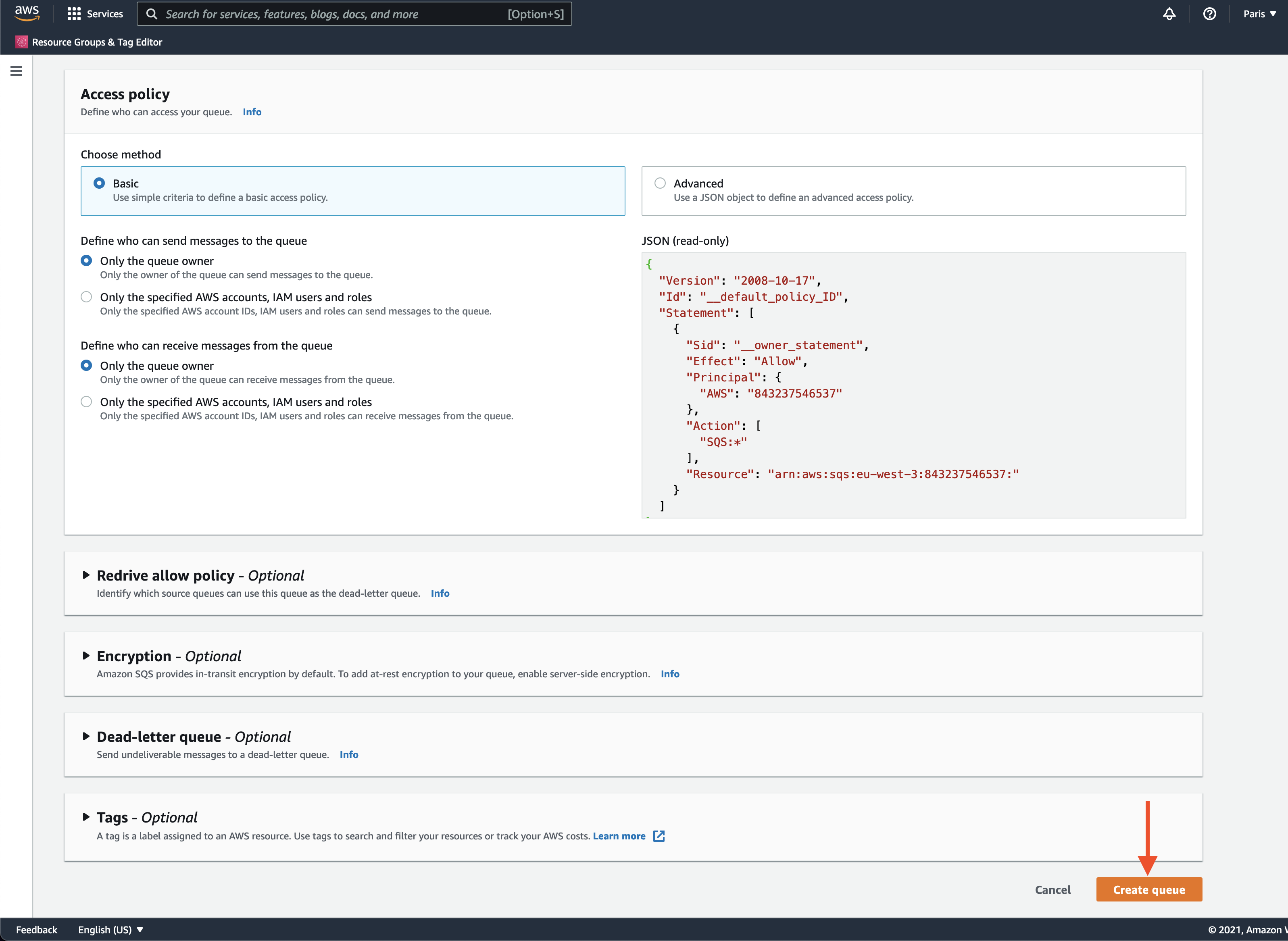
We will use the Standard queue and leave all the settings in defaults for now. Type in the name of the queue and click Create.
Create Message Producer
In this step, we will deploy an app that pushes messages to the SQS queue. The source code of the app is available here.
The source code of the app is simple - it's a web server that sends messages to the SQS queue each time someone hits its API endpoint:
const command = new SendMessageCommand({});client.send(command).then((data) => {console.log(data);res.end('Success');// process data.},(error) => {console.error(error);res.end('Error');// error handling.});
To deploy the app on Qovery, all you need to do is to fork the repository from above and create a new app adding port 3000:
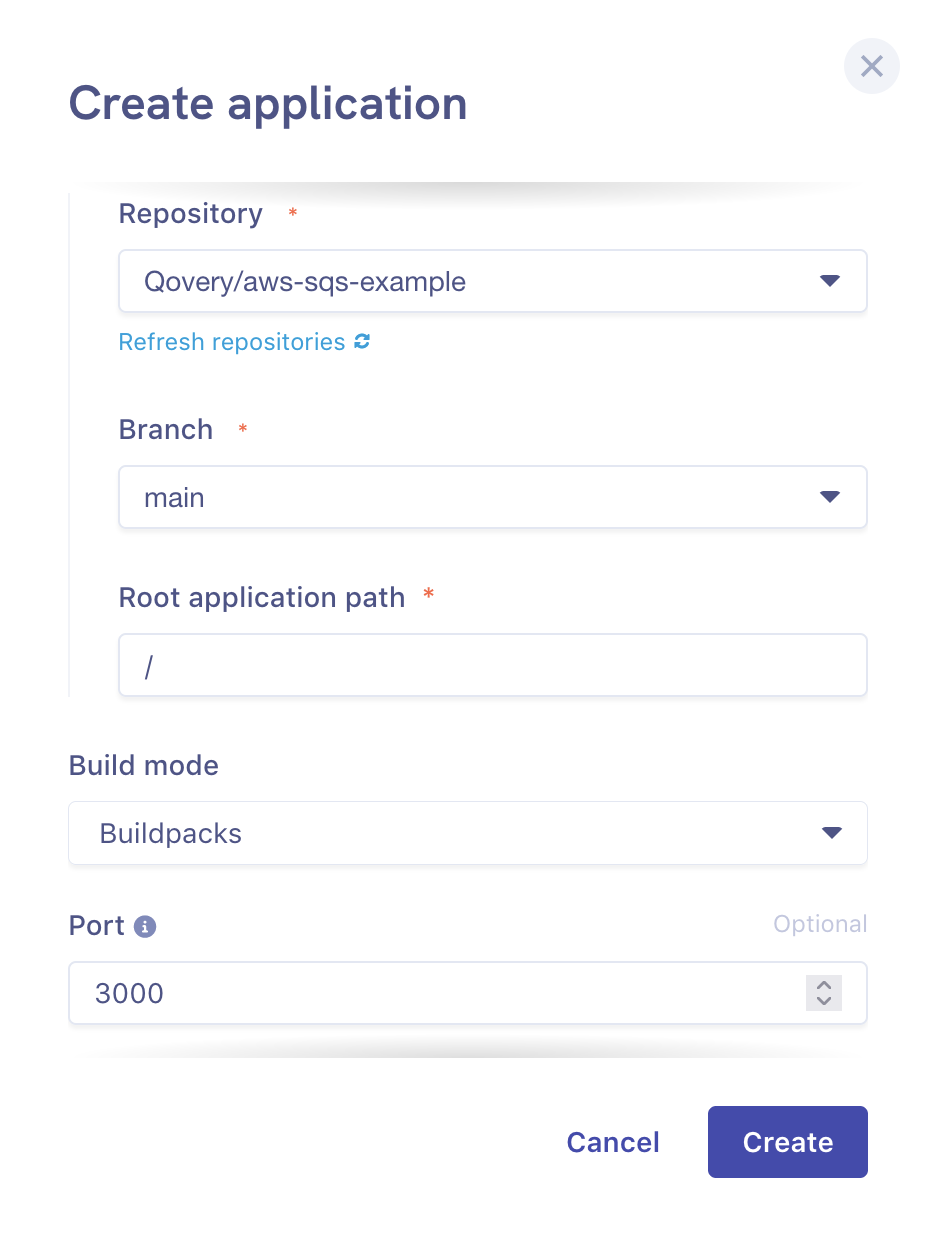
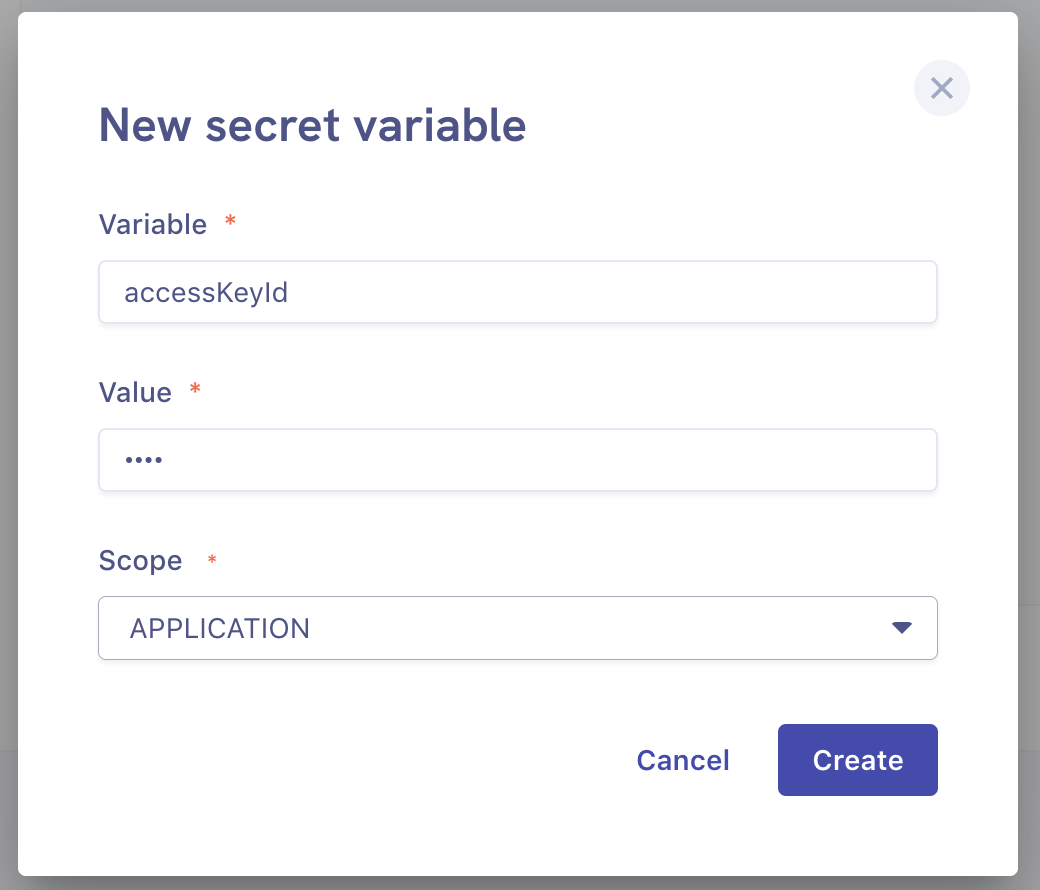
Afterwards, we need to add two environment variables:
accessKeyId- your AWS access key IDsecretAccessKey- your AWS secret access key
You can add them in Environment Variebles Secret section in your application settings:
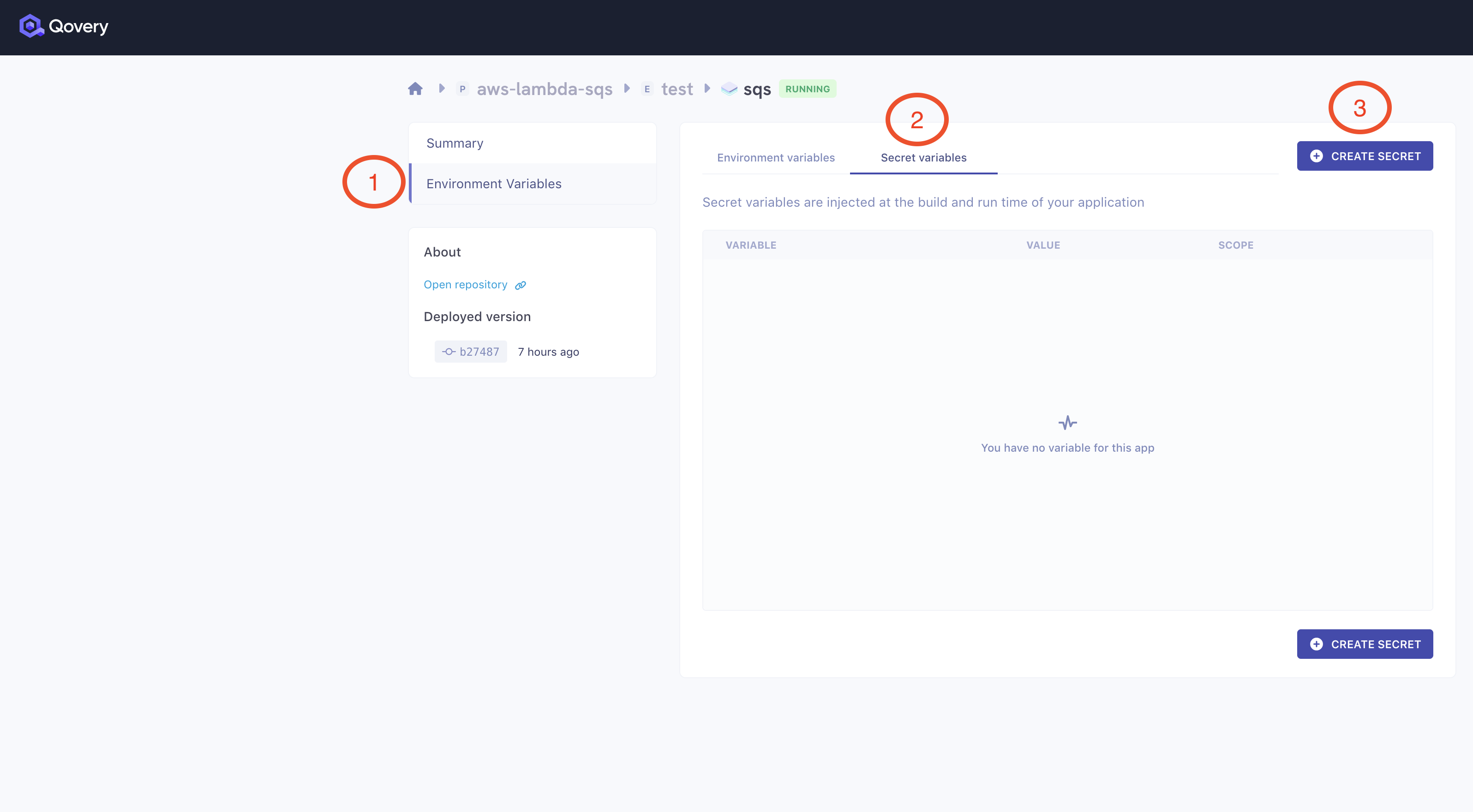
After all the setup is all done, click the Deploy button - the application will be shortly deployed.
Create Lambda Consumers
In AWS Console, open AWS Lambda panel.
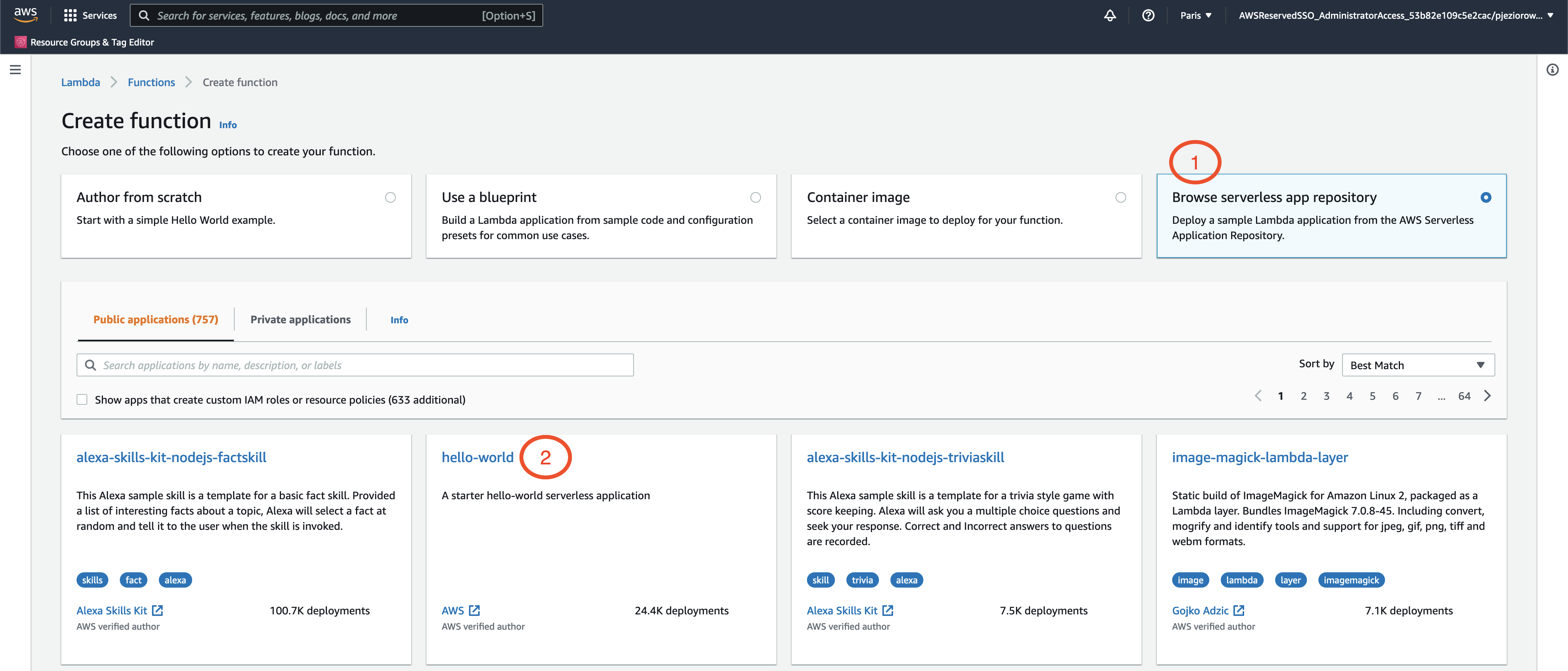
For the sake of the guide, we will use a simple hello-world lambda from AWS serverless app repository.
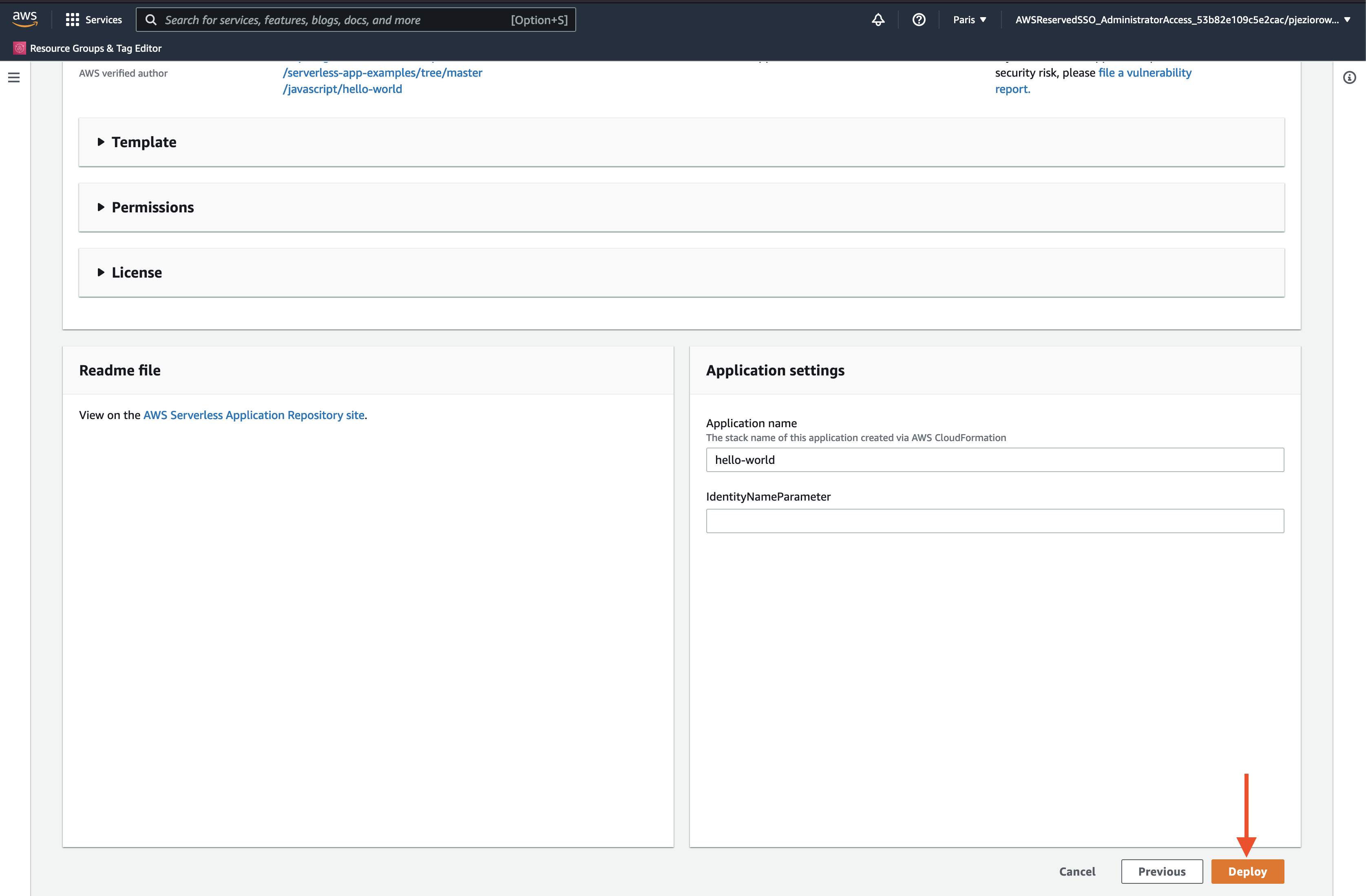
Browse the app repository and pick the hello-world function as shown in the screenshot above, and deploy the function
Create Lambda Trigger
To make our Lambdas consume messages from SQS, we will need to add a Lambda Trigger in the SQS configuration.
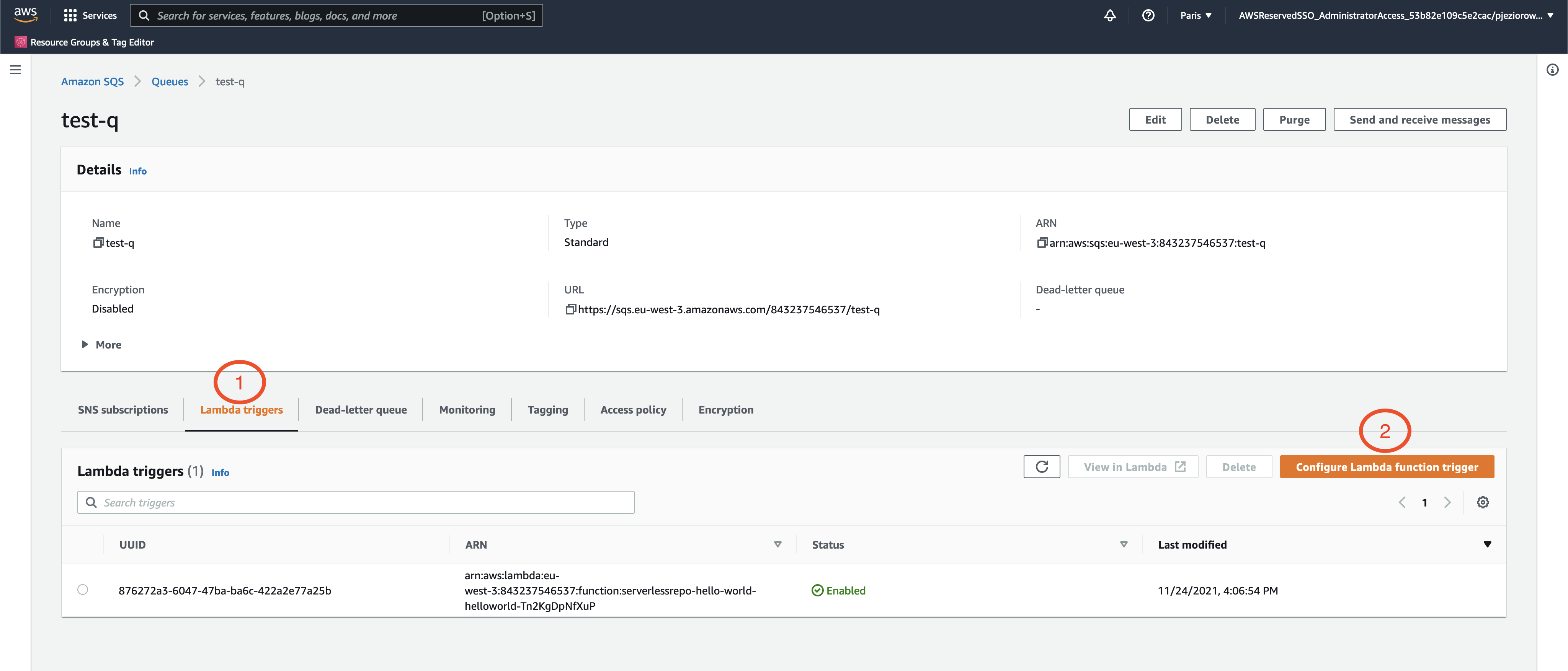
Click on Configure Lambda Function Trigger as shown in the screenshot above and select your lambda function from the dropdown, then save the changes:
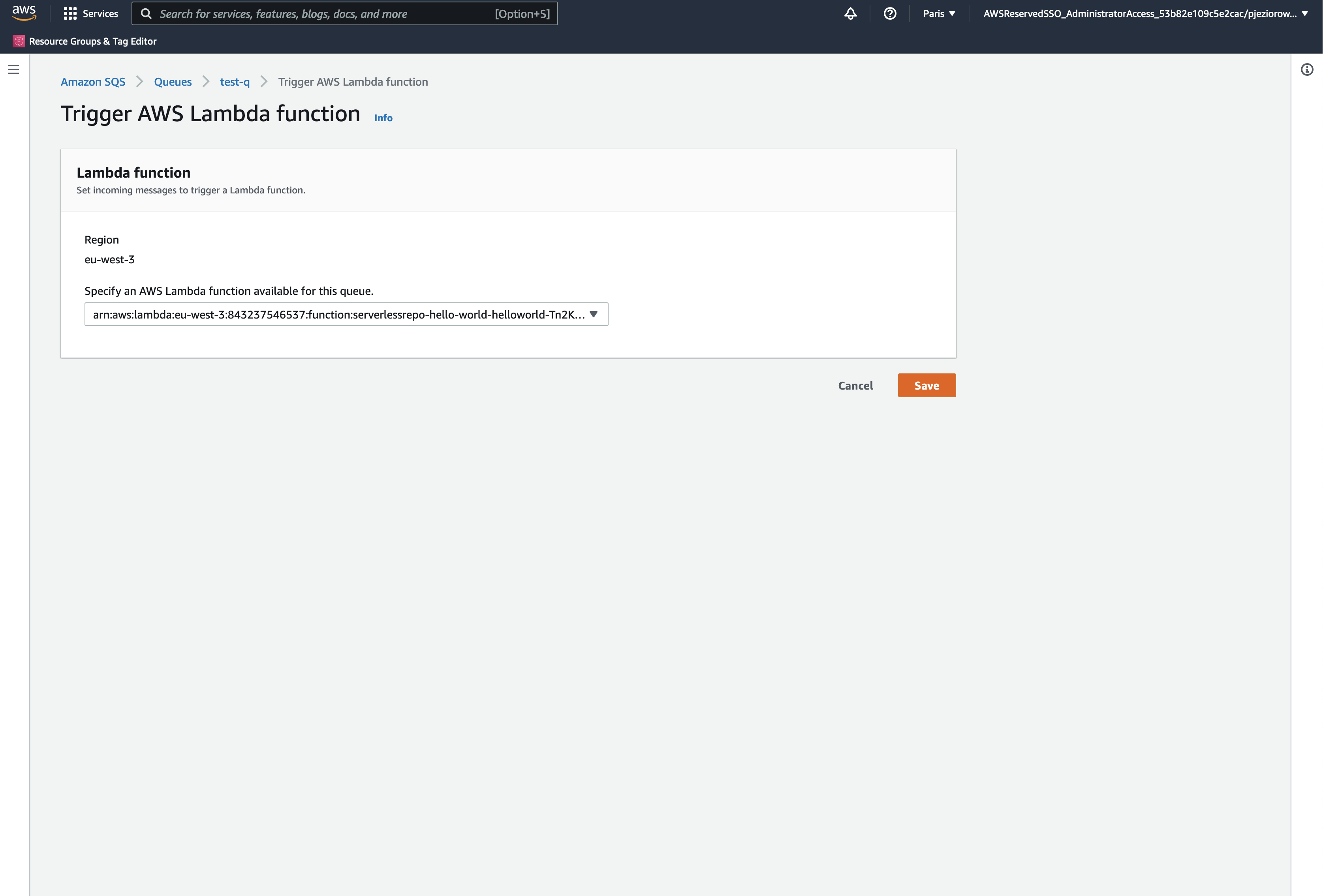
Configure Permissions
Let's now grant our Lambda functions access to the SQS queue we created before.
In our lambda view, click on Configure:
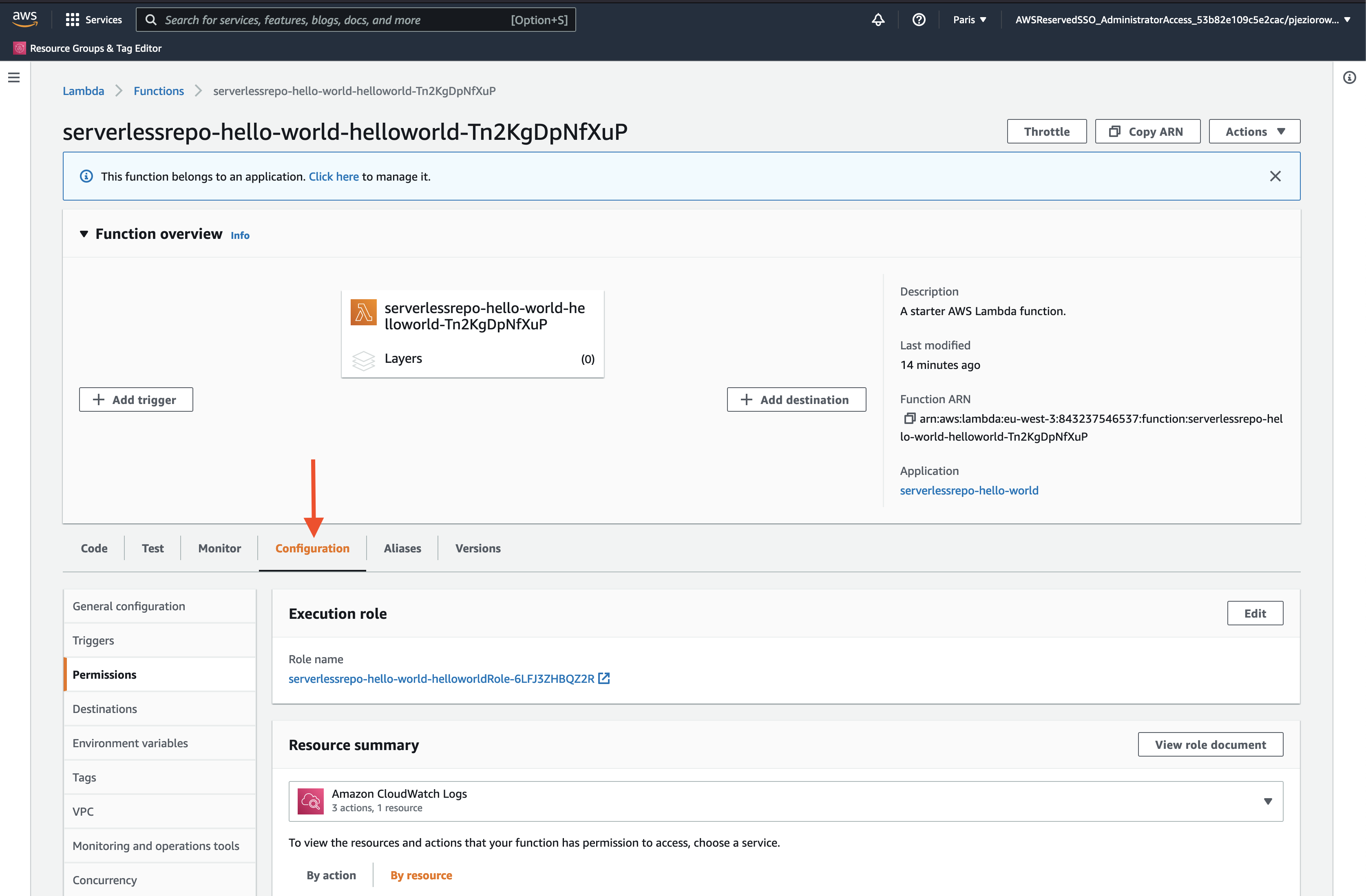
Then, click on a role in Execution role to get redirected to a view where we can alter our Lambda permissions.
In the role summary screen, click on Edit policy next to helloWorldrolePolicy
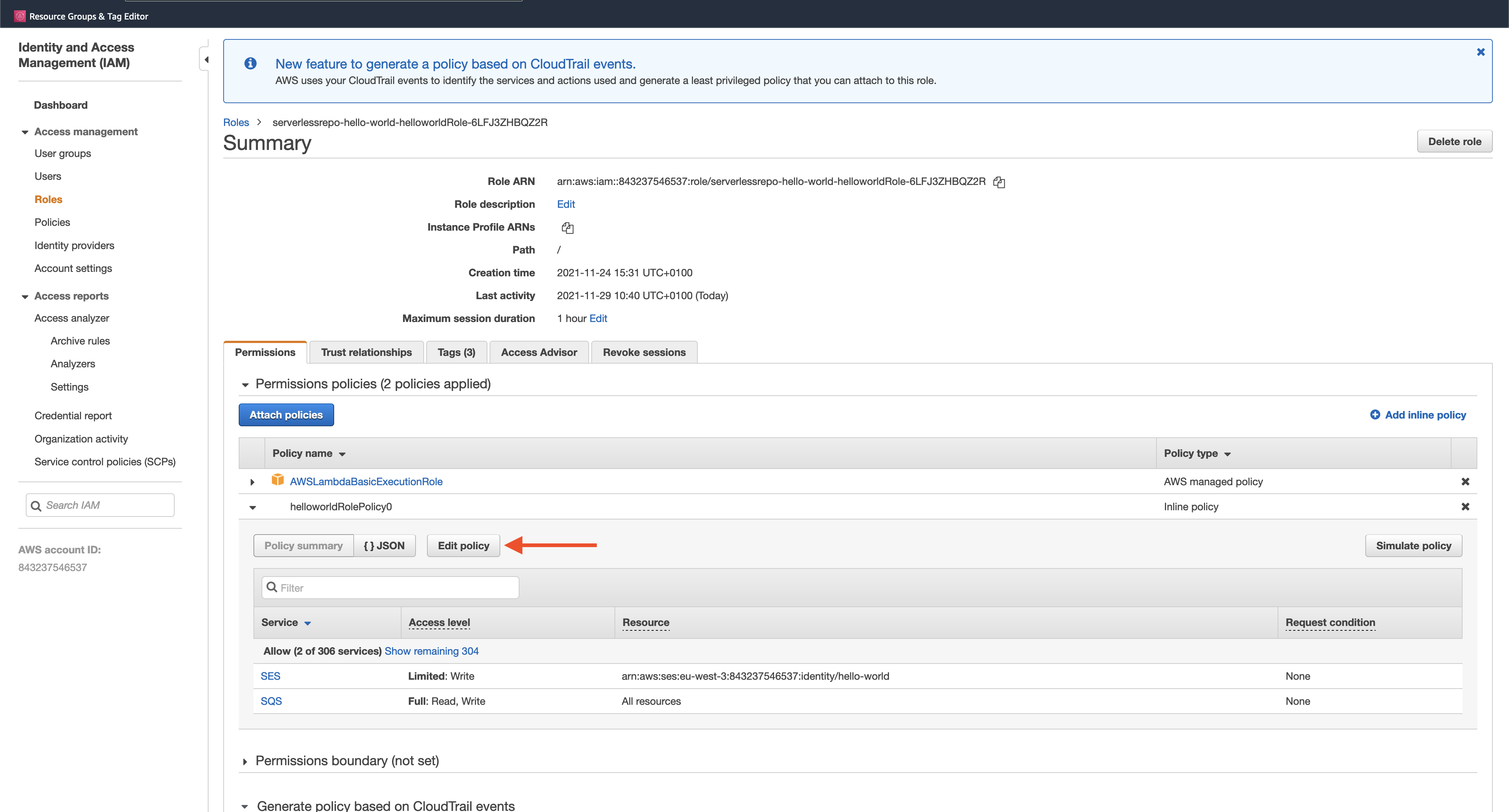
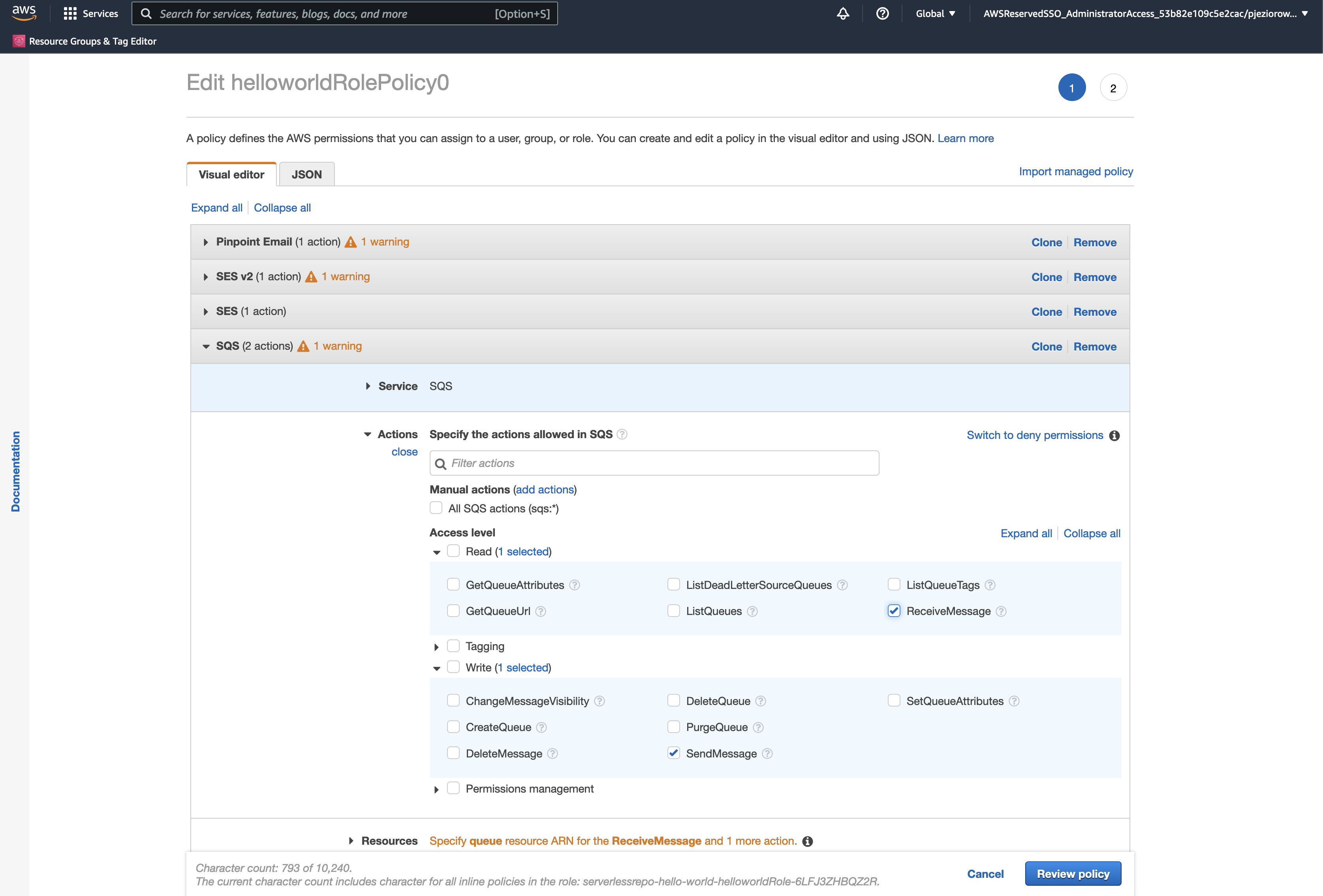
In the SQS section, grant permissions to all Read/Write options in the Actions Access level and accept the changes:
Test Lambda as an SQS Consumer Flow
To push messages to our SQS queue from the backend app deployed on Qovery, click on the Open button in the application we deployed in the previous step. It will redirect you to the API endpoint exposed by the backend app - the logic inside the application is made so that it sends messages to the SQS queue.
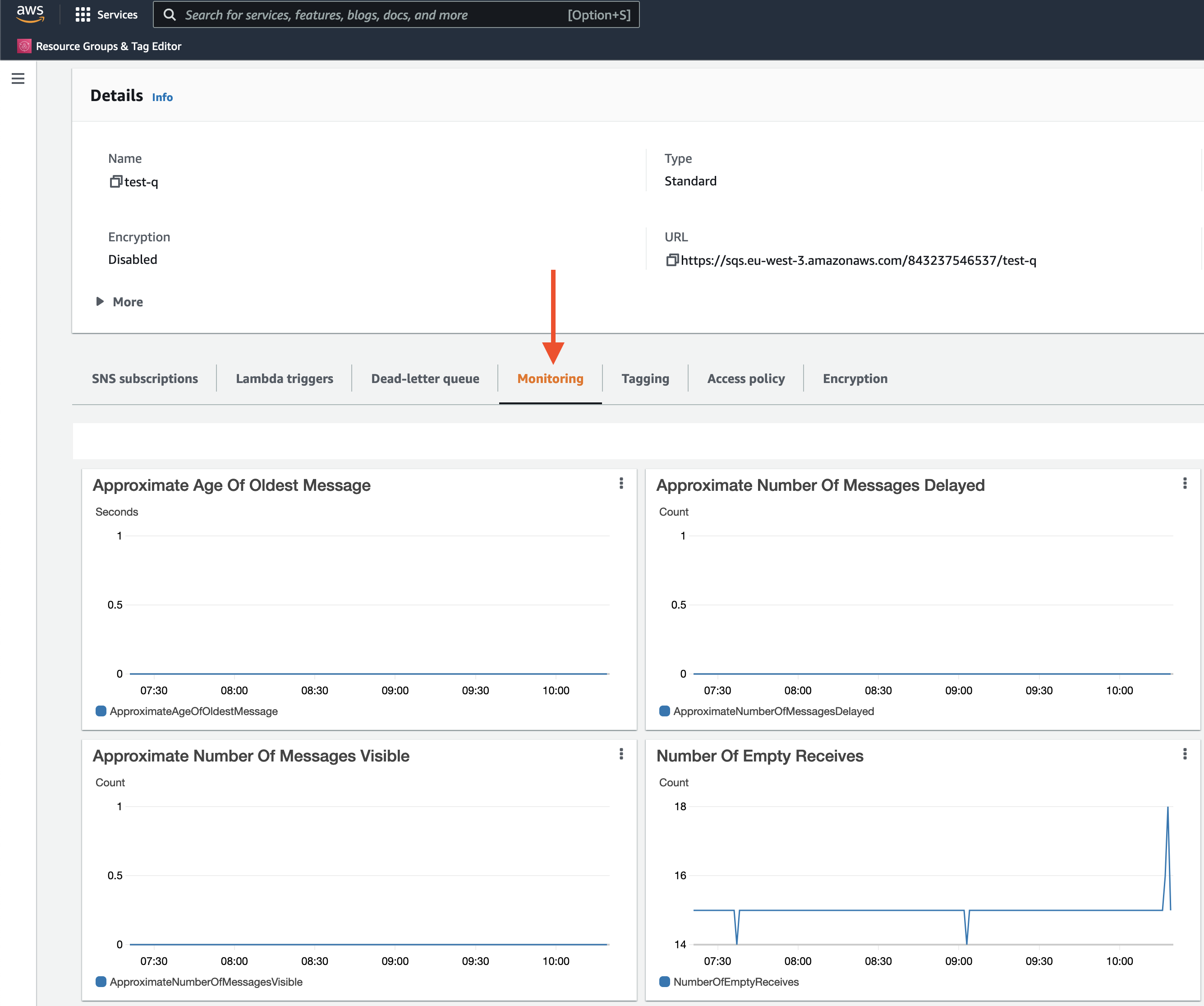
Now, in the Monitoring section of SQS in AWS Console, we will see messages received on metrics charts:
To validate that our consumer Lambdas processed the messages, navigate to your lambda Monitor panel:
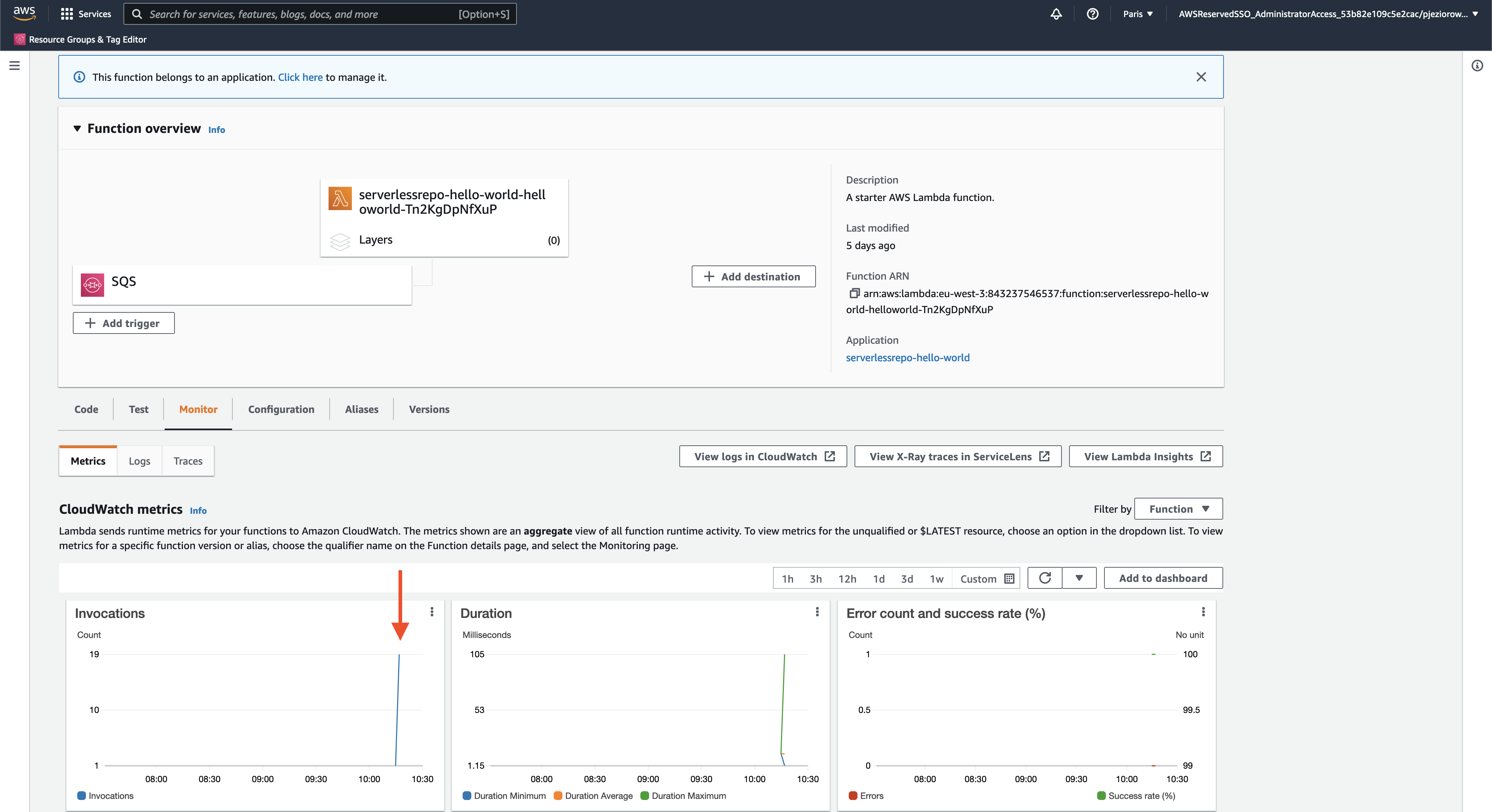
In the Invocations chart, you'll notice that our Lambda was triggered several times by the messages sent over the SQS.
Conclusions
In this part of the tutorial, we learned how to send messages over from an application deployed on Qovery to SQS and consume them from serverless Lambda functions. In the next part, we will create a scalable group of worker applications deployed by Qovery that consume messages from the same Queue.