In this tutorial, we will walk you through configuring IP and HTTP header-based authorization on your service running on Qovery Managed Cluster. This setup is particularly useful for multi-tenant systems, where access to different workspaces or services depends on a combination of the client's IP address and a specific header.
Before you begin, this guide assumes the following:
- Your service is running on a Qovery managed cluster.
Goal
This tutorial will cover how to setup IP and HTTP header-based authorization on your services by customizing Nginx configuration.
Here's the business requirement we have for this tutorial:
All incoming requests come with a custom HTTP header
X-QOVERY-SOURCErepresenting source of the request, let's say it can be one of the following values:staging,productionordevelopment.Every Qovery source has a specific IP range:
staging:10.42.0.0/16,10.43.0.0/16production:10.44.0.0/16development:92.xxx.xx.171(my office IP address, I will use to test the setup)
Every request coming from an address IP not in the range of the source should be rejected.
Reject any requests without the
X-QOVERY-SOURCEheader.
Initial setup
Configure cluster
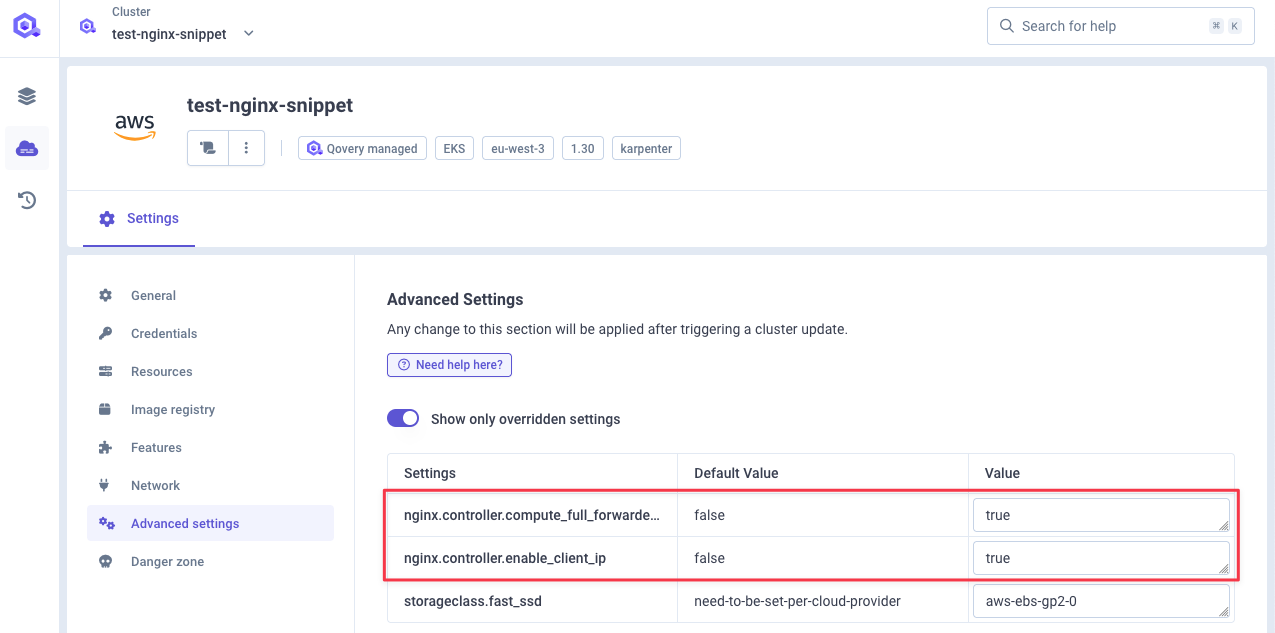
For this example, I will configure Nginx to enable nginx.controller.enable_client_ip and nginx.controller.compute_full_forwarded_for. It will allow me to better illustrate the whitelist configuration.
Configure service
I will use a basic container service echo-server setup with Qovery. This service is listening on port 80.
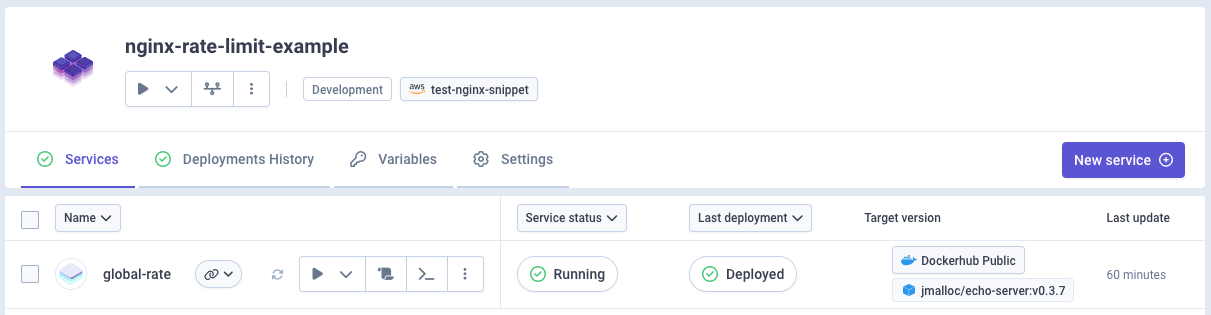
To start with, this service don't have any whitelisting in place, everything will be accepted.
Testing querying the service
Testing the service to make sure it's working as expected.
❯ curl -v -s https://p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh/* Trying 52.47.212.175:443...* Connected to p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh (52.47.212.175) port 443* ALPN: curl offers h2,http/1.1* (304) (OUT), TLS handshake, Client hello (1):* CAfile: /etc/ssl/cert.pem* CApath: none* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Server hello (2):* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Unknown (8):* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, CERT verify (15):* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Finished (20):* (304) (OUT), TLS handshake, Finished (20):* SSL connection using TLSv1.3 / AEAD-AES256-GCM-SHA384* ALPN: server accepted h2* Server certificate:* subject: CN=*.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh* start date: Dec 30 08:35:19 2024 GMT* expire date: Mar 30 08:35:18 2025 GMT* subjectAltName: host "p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh" matched cert's "*.z77ccfcb8.sl* issuer: C=US; O=Let's Encrypt; CN=R11* SSL certificate verify ok.* using HTTP/2* [HTTP/2] [1] OPENED stream for https://p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh/* [HTTP/2] [1] [:method: GET]* [HTTP/2] [1] [:scheme: https]* [HTTP/2] [1] [:authority: p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh]* [HTTP/2] [1] [:path: /]* [HTTP/2] [1] [user-agent: curl/8.4.0]* [HTTP/2] [1] [accept: */*]> GET / HTTP/2> Host: p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh> User-Agent: curl/8.4.0> Accept: */*>< HTTP/2 200< date: Sun, 12 Jan 2025 15:31:07 GMT< content-type: text/plain< content-length: 429< strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains<Request served by app-zc6971a47-service-example-66b74b556d-l4kk6GET / HTTP/1.1Host: p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.shAccept: */*User-Agent: curl/8.4.0X-Forwarded-For: 92.xxx.xx.171X-Forwarded-Host: p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.shX-Forwarded-Port: 443X-Forwarded-Proto: httpsX-Forwarded-Scheme: httpsX-Real-Ip: 92.xxx.xx.171X-Request-Id: 9e0119afcd2fcbb1b45ac1131ba82a15X-Scheme: https* Connection #0 to host p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh left intactAll good!
Configuring IP and HTTP header-based authorization
Declare whitelisting configuration at cluster level
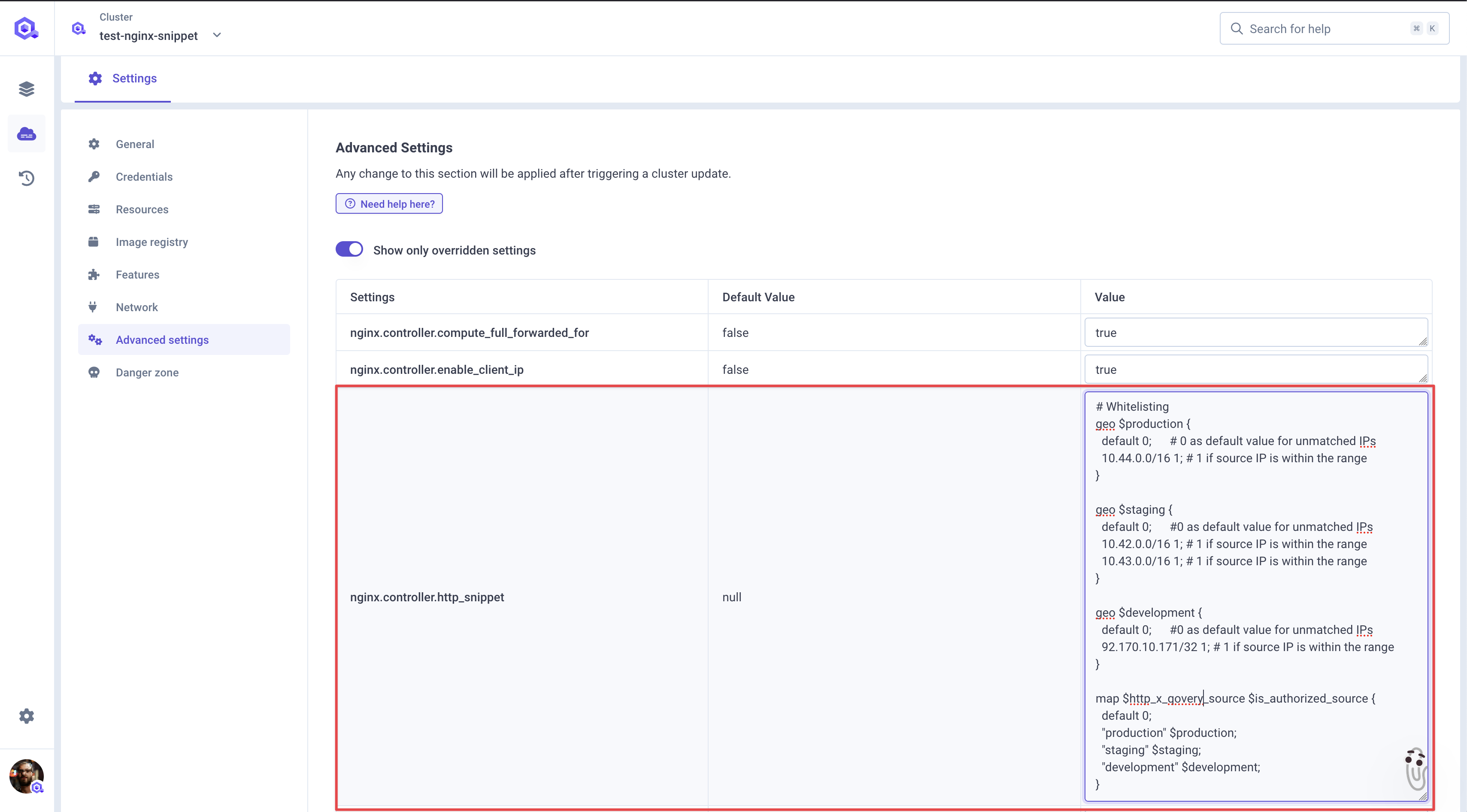
In order to set a whitelisting configuration, we need to declare it at cluster level in cluster advanced settings
nginx.controller.http_snippet(see documentation).Here's nginx
nginx.controller.http_snippetvalue we will set:Details# Whitelistinggeo $production {default 0; # 0 as default value for unmatched IPs10.44.0.0/16 1; # 1 if source IP is within the range}geo $staging {default 0; # 0 as default value for unmatched IPs10.42.0.0/16 1; # 1 if source IP is within the range10.43.0.0/16 1; # 1 if source IP is within the range}geo $development {default 0; # 0 as default value for unmatched IPs92.xxx.xx.171/32 1; # 1 if source IP is this exact IP (some values were replaced by x for privacy)}map $http_x_qovery_source $is_authorized_source {default 0;"production" $production;"staging" $staging;"development" $development;}- The
geodirective creates variables based on the client's IP address, allowing you to classify them into groups. In this case, thegeoblocks define access for production and staging environments.geo $production: creates a variable $production to determine if the client IP is part of the allowed range.default 0;: default value is0, meaning any IP that does not match explicitly will be denied.10.44.0.0/16 1:10.44.0.0/16range is assigned the value1, meaning it's allowed.
geo $staging: creates a variable $staging.default 0;: default value is0, meaning any IP that does not match explicitly will be denied.10.43.0.0/16 1:10.43.0.0/16range is assigned the value1, meaning it's allowed.10.42.0.0/16 1:10.42.0.0/16range is assigned the value1, meaning it's allowed.
geo $development: creates a variable $development to determine if the client IP is part of the allowed range.default 0;: default value is0, meaning any IP that does not match explicitly will be denied.92.xxx.xx.171/32 1:92.xxx.xx.171/32IP is assigned the value1, meaning it's allowed.
- The
mapdirective is used to derive a new variable ($is_authorized_source) based on the value of another variable ($http_x_qovery_source).map $http_x_qovery_source $is_authorized_source: the value of theX-Qovery-SourceHTTP header ($http_x_qovery_source) determines the$is_authorized_sourcevariable.default 0;: if theX-Qovery-Sourceheader does not match any specified key,$is_authorized_sourceis set to0."production" $production: ifX-Qovery-Sourceis"production", the$is_authorized_sourcewill take the value of$production(either0or1, depending on the client's IP range)."staging" $staging: similarly, ifX-Qovery-Sourceis"staging",$is_authorized_sourcewill take the value of$staging"development" $development: similarly, ifX-Qovery-Sourceis"development",$is_authorized_sourcewill take the value of$development
- The
Use this whitelisting rule in cluster configuration
Now that our whitelisting rule is defined, let use it in our cluster configuration.
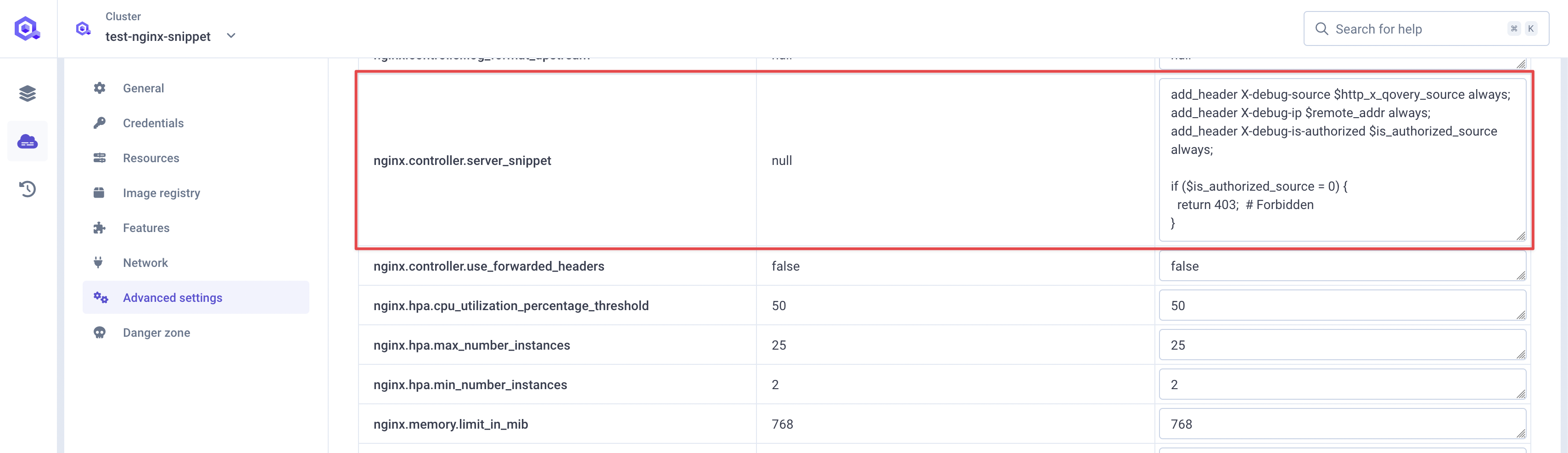
In order to do so, we need to declare this server snippet at cluster level in advanced settings
nginx.controller.server_snippet(see documentation):Detailsadd_header X-debug-source $http_x_qovery_source always;add_header X-debug-ip $remote_addr always;add_header X-debug-is-authorized $is_authorized_source always;if ($is_authorized_source = 0) {return 403; # Forbidden}This snippet will return an HTTP
403for any request that does not match the whitelisting rule we defined earlier. In order to ease setup and debug, I've added some headers to the response:X-debug-source: the value of theX-Qovery-Sourceheader.X-debug-ip: the client's IP address.X-debug-is-authorized: whether the request is authorized or not.
Deploy your cluster
You can now deploy your cluster with the new settings.
Testing the whitelist rule
Let's test our setup
Case 1: No header, IP outside any whitelisted ranges
For this test, I will send a request without the
X-QOVERY-SOURCEheader and from an IP address outside the allowed ranges.❯ curl -v -s https://p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh/* Trying 13.38.142.29:443...* Connected to p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh (13.38.142.29) port 443* ALPN: curl offers h2,http/1.1* (304) (OUT), TLS handshake, Client hello (1):* CAfile: /etc/ssl/cert.pem* CApath: none* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Server hello (2):* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Unknown (8):* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, CERT verify (15):* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Finished (20):* (304) (OUT), TLS handshake, Finished (20):* SSL connection using TLSv1.3 / AEAD-AES256-GCM-SHA384* ALPN: server accepted h2* Server certificate:* subject: CN=*.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh* start date: Dec 30 08:35:19 2024 GMT* expire date: Mar 30 08:35:18 2025 GMT* subjectAltName: host "p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh" matched cert's "*.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh"* issuer: C=US; O=Let's Encrypt; CN=R11* SSL certificate verify ok.* using HTTP/2* [HTTP/2] [1] OPENED stream for https://p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh/* [HTTP/2] [1] [:method: GET]* [HTTP/2] [1] [:scheme: https]* [HTTP/2] [1] [:authority: p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh]* [HTTP/2] [1] [:path: /]* [HTTP/2] [1] [user-agent: curl/8.4.0]* [HTTP/2] [1] [accept: */*]> GET / HTTP/2> Host: p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh> User-Agent: curl/8.4.0> Accept: */*>< HTTP/2 403< date: Sun, 12 Jan 2025 15:49:20 GMT< content-type: text/html< content-length: 146< x-debug-ip: 45.84.136.102< x-debug-is-authorized: 0<<html><head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head><body><center><h1>403 Forbidden</h1></center><hr><center>nginx</center></body></html>* Connection #0 to host p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh left intactAs we can see I've got an HTTP
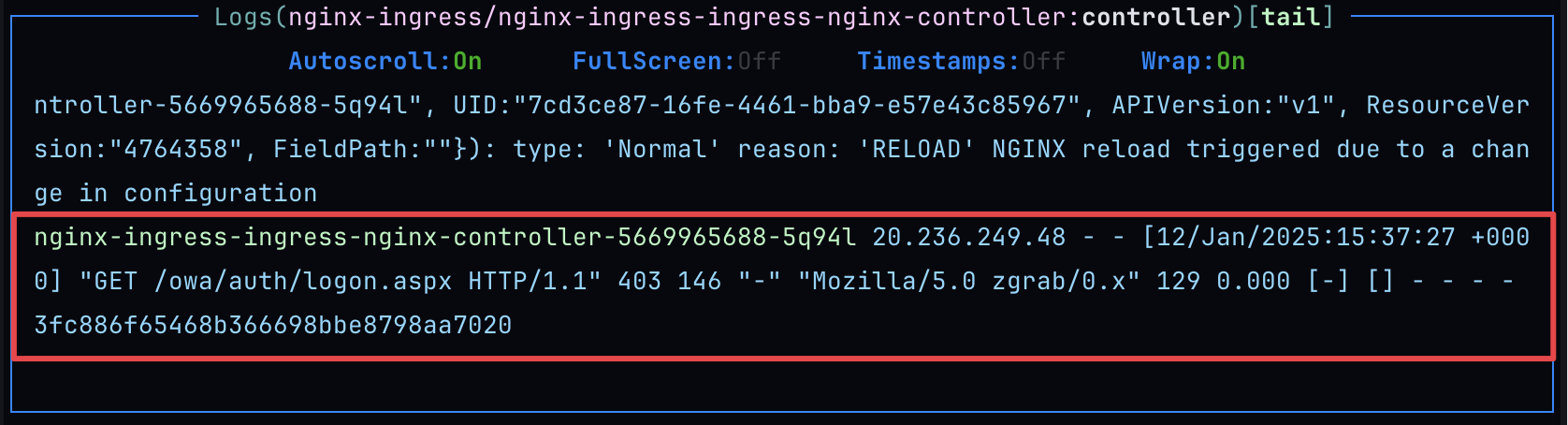
403status code, meaning the request was rejected.Debug headers values:
< x-debug-ip: 45.84.136.102< x-debug-is-authorized: 0NGINX controller logs showing the request was rejected.
Case 2: Header
production, IP outside any whitelisted rangesFor this test, I will send a request with the
X-QOVERY-SOURCE: productionheader and from an IP address outside the allowed ranges.❯ curl -v -H 'X-QOVERY-SOURCE: production' -s https://p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh/* Trying 13.38.142.29:443...* Connected to p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh (13.38.142.29) port 443* ALPN: curl offers h2,http/1.1* (304) (OUT), TLS handshake, Client hello (1):* CAfile: /etc/ssl/cert.pem* CApath: none* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Server hello (2):* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Unknown (8):* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, CERT verify (15):* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Finished (20):* (304) (OUT), TLS handshake, Finished (20):* SSL connection using TLSv1.3 / AEAD-AES256-GCM-SHA384* ALPN: server accepted h2* Server certificate:* subject: CN=*.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh* start date: Dec 30 08:35:19 2024 GMT* expire date: Mar 30 08:35:18 2025 GMT* subjectAltName: host "p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh" matched cert's "*.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh"* issuer: C=US; O=Let's Encrypt; CN=R11* SSL certificate verify ok.* using HTTP/2* [HTTP/2] [1] OPENED stream for https://p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh/* [HTTP/2] [1] [:method: GET]* [HTTP/2] [1] [:scheme: https]* [HTTP/2] [1] [:authority: p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh]* [HTTP/2] [1] [:path: /]* [HTTP/2] [1] [user-agent: curl/8.4.0]* [HTTP/2] [1] [accept: */*]* [HTTP/2] [1] [x-qovery-source: production]> GET / HTTP/2> Host: p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh> User-Agent: curl/8.4.0> Accept: */*> X-QOVERY-SOURCE: production>< HTTP/2 403< date: Sun, 12 Jan 2025 15:59:54 GMT< content-type: text/html< content-length: 146< x-debug-source: production< x-debug-ip: 45.84.136.102< x-debug-is-authorized: 0<<html><head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head><body><center><h1>403 Forbidden</h1></center><hr><center>nginx</center></body></html>* Connection #0 to host p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh left intactAs we can see I've got an HTTP
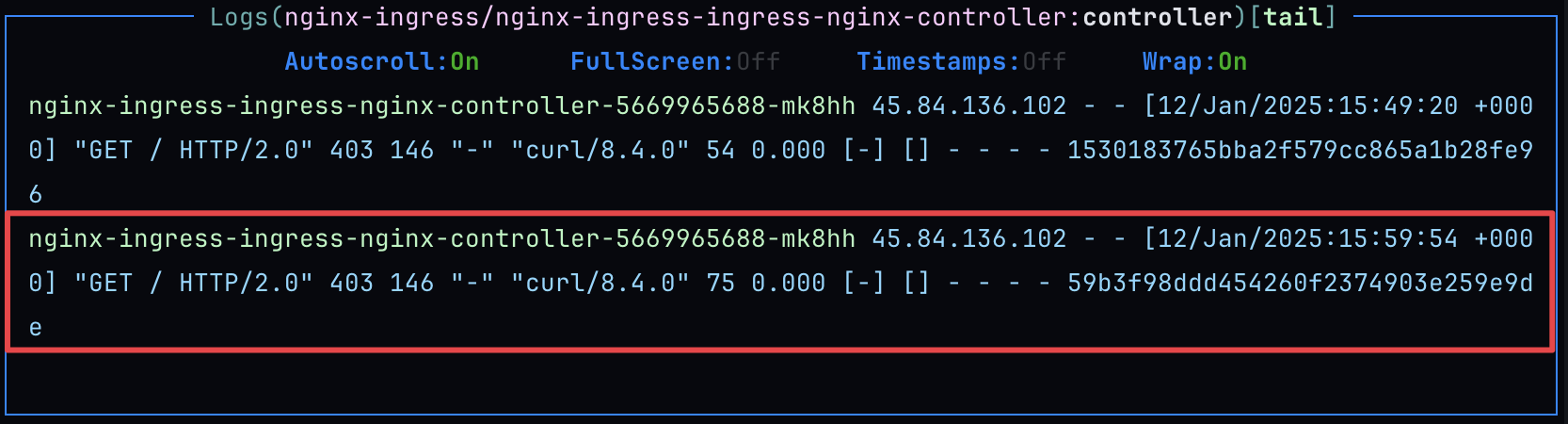
403status code, meaning the request was rejected.Debug headers values:
< x-debug-source: production< x-debug-ip: 45.84.136.102< x-debug-is-authorized: 0NGINX controller logs showing the request was rejected.
Case 3: Header
development, IP inside whitelisted rangesFor this test, I will send a request with the
X-QOVERY-SOURCE: developmentheader and from an IP address inside the allowed ranges.documentation main* ≡2h3m18s❯ curl -v -H 'X-QOVERY-SOURCE: development' -s https://p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh/* Trying 13.38.142.29:443...* Connected to p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh (13.38.142.29) port 443* ALPN: curl offers h2,http/1.1* (304) (OUT), TLS handshake, Client hello (1):* CAfile: /etc/ssl/cert.pem* CApath: none* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Server hello (2):* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Unknown (8):* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, CERT verify (15):* (304) (IN), TLS handshake, Finished (20):* (304) (OUT), TLS handshake, Finished (20):* SSL connection using TLSv1.3 / AEAD-AES256-GCM-SHA384* ALPN: server accepted h2* Server certificate:* subject: CN=*.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh* start date: Dec 30 08:35:19 2024 GMT* expire date: Mar 30 08:35:18 2025 GMT* subjectAltName: host "p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh" matched cert's "*.z77ccfcb8.sl* issuer: C=US; O=Let's Encrypt; CN=R11* SSL certificate verify ok.* using HTTP/2* [HTTP/2] [1] OPENED stream for https://p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh/* [HTTP/2] [1] [:method: GET]* [HTTP/2] [1] [:scheme: https]* [HTTP/2] [1] [:authority: p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh]* [HTTP/2] [1] [:path: /]* [HTTP/2] [1] [user-agent: curl/8.4.0]* [HTTP/2] [1] [accept: */*]* [HTTP/2] [1] [x-qovery-source: development]> GET / HTTP/2> Host: p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh> User-Agent: curl/8.4.0> Accept: */*> X-QOVERY-SOURCE: development>< HTTP/2 200< date: Sun, 12 Jan 2025 20:05:32 GMT< content-type: text/plain< content-length: 458< strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains< x-debug-source: development< x-debug-ip: 92.xxx.xx.171< x-debug-is-authorized: 1<Request served by app-zc6971a47-service-example-66b74b556d-l4kk6GET / HTTP/1.1Host: p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.shAccept: */*User-Agent: curl/8.4.0X-Forwarded-For: 92.xxx.xx.171X-Forwarded-Host: p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.shX-Forwarded-Port: 443X-Forwarded-Proto: httpsX-Forwarded-Scheme: httpsX-Qovery-Source: developmentX-Real-Ip: 92.xxx.xx.171X-Request-Id: ce6b9567bac12b64a5b161dc8df3d0f9X-Scheme: https* Connection #0 to host p8080-zdb6be5b9-z928629ac-gtw.z77ccfcb8.slab.sh left intactAs we can see I've got an HTTP
403status code, meaning the request was rejected.Debug headers values:
< x-debug-source: development< x-debug-ip: 92.xxx.xx.171< x-debug-is-authorized: 1
Conclusion
With the nginx.controller.http_snippet and nginx.controller.server_snippet cluster advanced settings, you can create powerful access control rules in NGINX that combine IP-based restrictions and HTTP header validation. This configuration is scalable and flexible for managing multi-tenant systems or any environment requiring complex authorization logic.
Feel free to adapt this setup to your specific needs, and always test thoroughly before deploying to production!