In this short guide, we'll go trough managing Secrets/Environment Variables in React applications created using create-react-app and deployed on Qovery.
Most of the guides you can find online propose quite complex solutions with creating your own bash scripts to set up env variables in apps created by create-react-app - this guide will show you an easier alternative and a way to Dockerize your React app in production-ready way.
Code Repository
In this guide we'll use https://github.com/pjeziorowski/cra-test repository - it's a sample application bootstrapped using npx create-react-app my-app command.
After the application structure is generated, we dockerize the application by adding a Dockerfile with the following content:
# Docker Image which is used as foundation to create# a custom Docker Image with this DockerfileFROM node:10# A directory within the virtualized Docker environmentWORKDIR /usr/src/app# Copies package.json and package-lock.json to Docker environmentCOPY package*.json ./# Installs all node packagesRUN npm install# Copies everything over to Docker environmentCOPY . .# Uses port which is used by the actual applicationEXPOSE 3000# Finally runs the applicationCMD [ "npm", "start" ]
One more little thing that we change is creating a new constant that uses a value of REACT_APP_MSG environment variable to print a text on the website:
const msg = process.env.REACT_APP_MSG
And then, we print it in the UI:
<aclassName="App-link"href="https://reactjs.org"target="_blank"rel="noopener noreferrer">{msg}</a>
Environment Variables
Let's now add a .env file for the default environment variables for our React app. For this, we create a .env file with the content:
HOST="0.0.0.0"PORT="3000"REACT_APP_MSG="From .env"
Warning!
For all custom environment variables in apps created via create-react-app, we need to use REACT_APP_ prefix in env var names - it's a requirement, if we don't follow the convention, variables will not be accessible in our application!
Also, remember that all the values are accessible on the client-side (browser). You should not use it for any data that your users should not access in the browser.
Deployment
Before overriding the default env vars hardcoded in our repository using Qovery, let's first deploy the app.
To do so, add a new application using the code from previous steps. When configuring the application, don't forget to:
- Use
Dockerbuild mode - Add port
3000to expose the app on the internet
After the application is created, click on the Deploy button in application actions.
In a few minutes, your application should be up and running:

As you see, the text in the link From .env file indicates that the value
Adding Environment Variable
Now, let's override our REACT_APP_MSG environment variable (and the text we display in the UI).
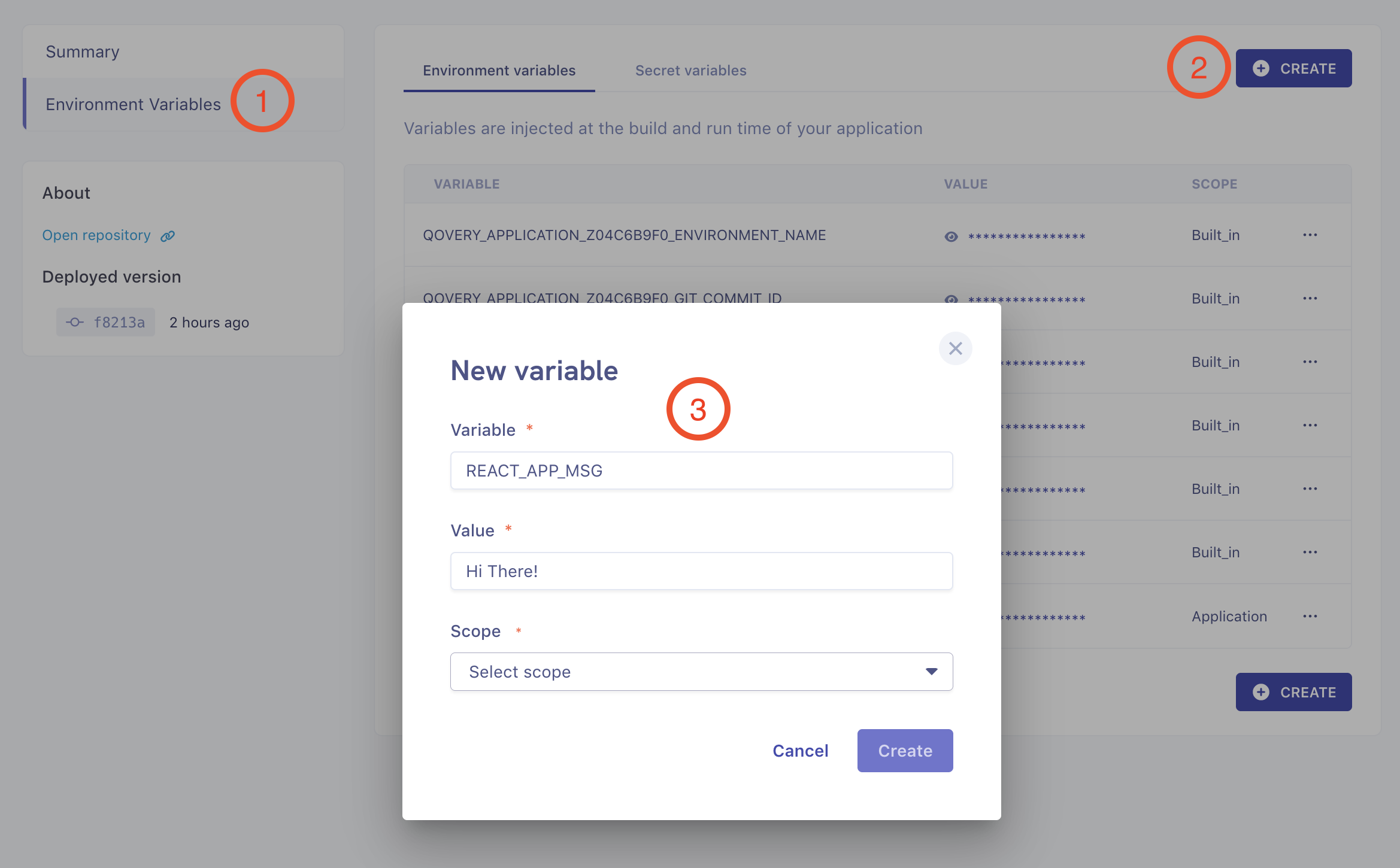
After adding a new variable, restart the application. In a minute or so, we should see that the message in our website is updated with the value of REACT_APP_MSG we added in Qovery Console:

Going Prod
To optimize our application for production usage, we’ll use a Nginx server to serve our frontend static content. To do so, we need to update our Dockerfile to the following:
FROM node:14-alpine AS builderENV NODE_ENV productionARG REACT_APP_MSGENV REACT_APP_MSG $REACT_APP_MSG# Add a work directoryWORKDIR /app# Cache and Install dependenciesCOPY package.json .COPY yarn.lock .RUN yarn install --production# Copy app filesCOPY . .# Build the appRUN yarn build# Bundle static assets with nginxFROM nginx:1.21.0-alpine as productionENV NODE_ENV production# Copy built assets from builderCOPY --from=builder /app/build /usr/share/nginx/html# Add your nginx.confCOPY nginx.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf# Expose portEXPOSE 3000# Start nginxCMD ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]
It uses a Nginx server for hosting your application instead of starting a Node.js server, which is more optimal for production usage.
Additionally, add a nginx.conf file with this content to configure your app:
server {listen 80;location / {root /usr/share/nginx/html/;include /etc/nginx/mime.types;try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;}}
Now, commit and push your changes - your create-react-app is handling env vars properly and is optimized for production usage.
Conclusion
In the guide, we went through managing environment variables in react / create-react-apps without resorting to using any bash scripts and host it on Qovery using Ngnix server.