Databases
Before you begin, this documentation assumes the following:
You have created an Environment.
Qovery natively lets you deploy and access the most popular SQL and NoSQL databases available on the major cloud providers. Reliability and resiliency are at the heart of their services, so you don't have to worry about your data on Qovery.
Qovery natively supports the following databases:
- PostgreSQL
- MySQL
- MongoDB
- Redis
Qovery can natively operate a database in two different ways (called "Mode"):
- Container mode: preferred for testing and development
- Managed mode: preferred for production, limited configuration parameters (see the Configuration section).
If the natively supported databases or operation modes are not enough for you, depending on your use case you have the following alternative solutions:
- Use an existing DB on a dedicated VPC: your applications can access this database via VPC peering. Have a look at this guide for more information.
- Create your custom database via Qovery: You will be able to deploy any kind of database through Qovery by using a lifecycle jobs. For example, you can use a terraform script to deploy your custom RDS instance on AWS via Terraform (have a look at this example).
The following sections will show you how you can create and manage the databases natively supported by Qovery. For any other use case, please refer to the guides provided above.
Container mode
The database is created as a container with attached persistent storage directly on your Kubernetes cluster (1 instance). They are perfect for development and testing, as they are significantly cheaper than services provided by cloud providers.
Managed mode
Qovery creates and manages the lifecycle of a cloud provider managed database instance (for example an RDS instance on AWS). These are perfect for production since they guarantee the right level of resilience, performance and data security best practices.
Applying changes to a managed database
Once you request to change the version, instance type or disk size of your Managed database, the cloud provider applies the update based on its own internal rules and might cause downtime of your database.
For example, by default AWS doesn't apply major updates immediately on the database and instead, it waits for a maintenance window. This means that your change will not be applied immediately but you can always force the change directly from your AWS console AFTER having applied the change on Qovery (to avoid configuration drifts).
Have a look at your cloud provider documentation to know more about how version upgrades are managed:
- AWS RDS DB engine upgrade: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/USER_UpgradeDBInstance.MySQL.html
- AWS maintenance window: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/USER_UpgradeDBInstance.Maintenance.html
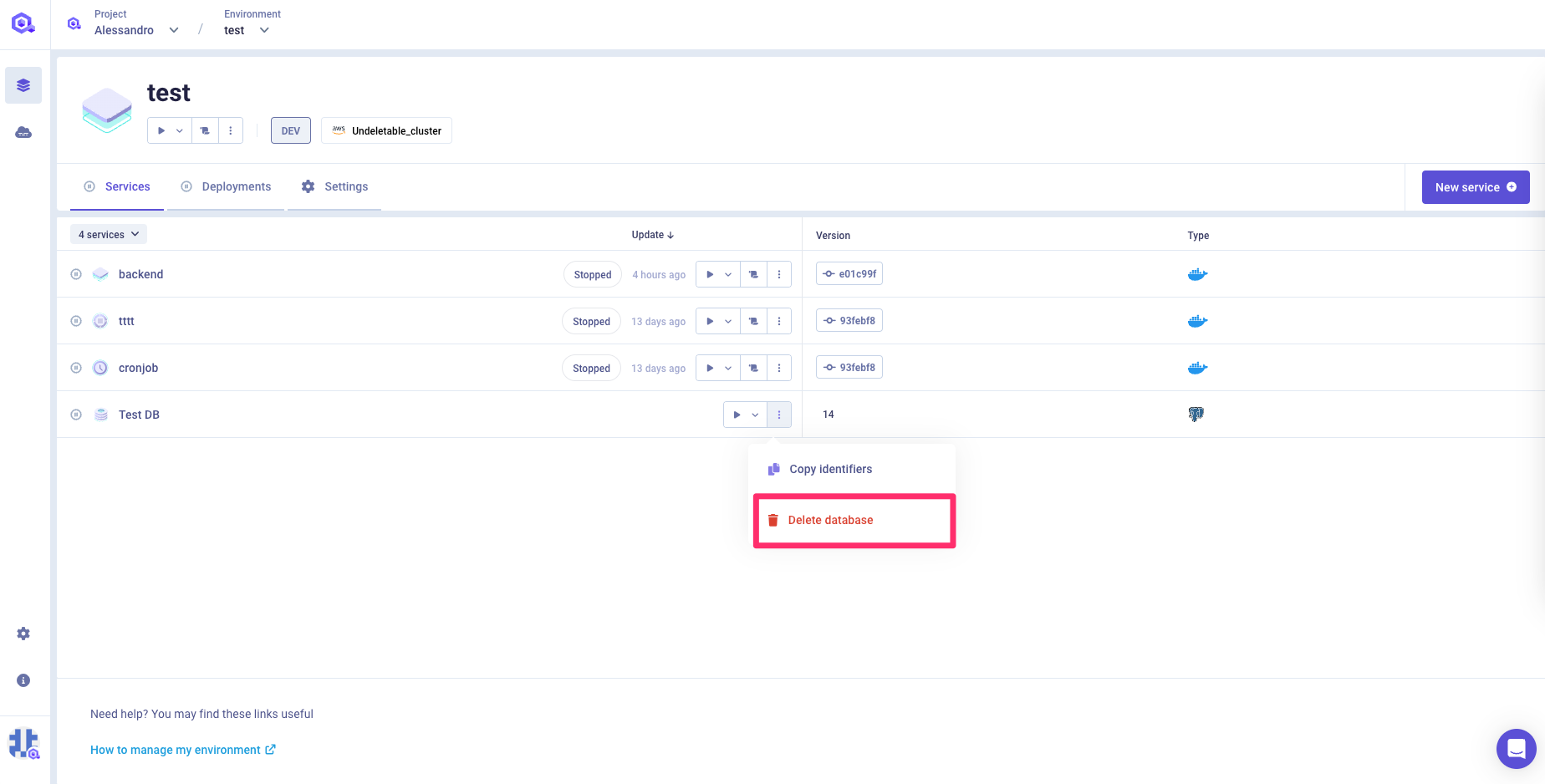
Create a database
Navigate to Console
Select your project and environment
Click
Add Databasebutton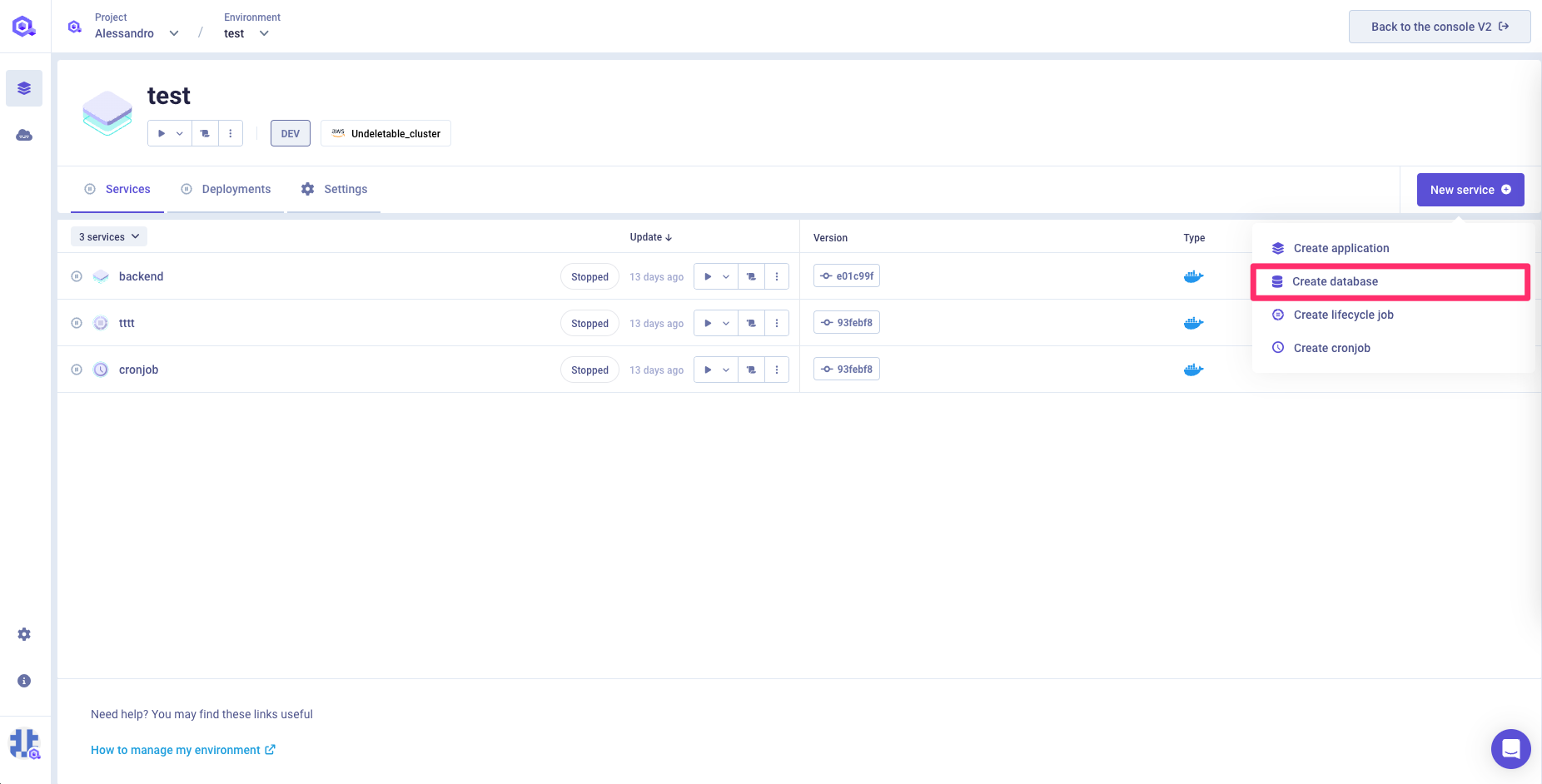
Select database type, name, description (optional), version, mode and accessibility
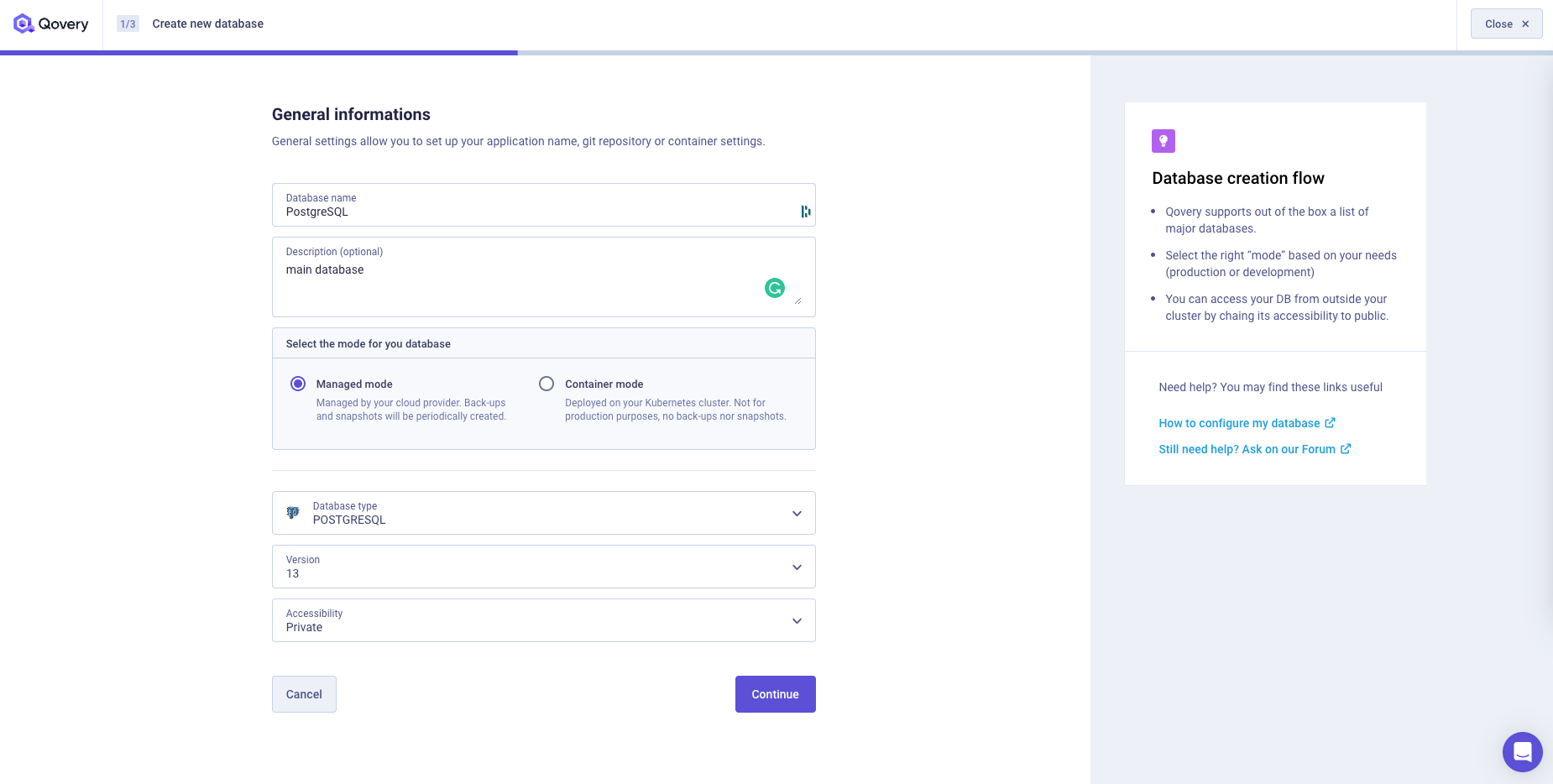
Extra labels/annotations (optional)
Add your extra annotation/label groups. See the Add annotation/label group section for more information. Annotation groups are not supported for managed databases.
Within the "Resources" step you will find different configurations based on the selected
mode:- If you are using the database in
Containermode, you can set the CPU, RAM and storage that will be assigned to the instance running the docker image of the database. - If you are using the database in
Managedmode, you can select the instance type and the storage that will be assigned to the instance running the database. Note, the instance selected instance type has a direct impact on your cloud provider cost.
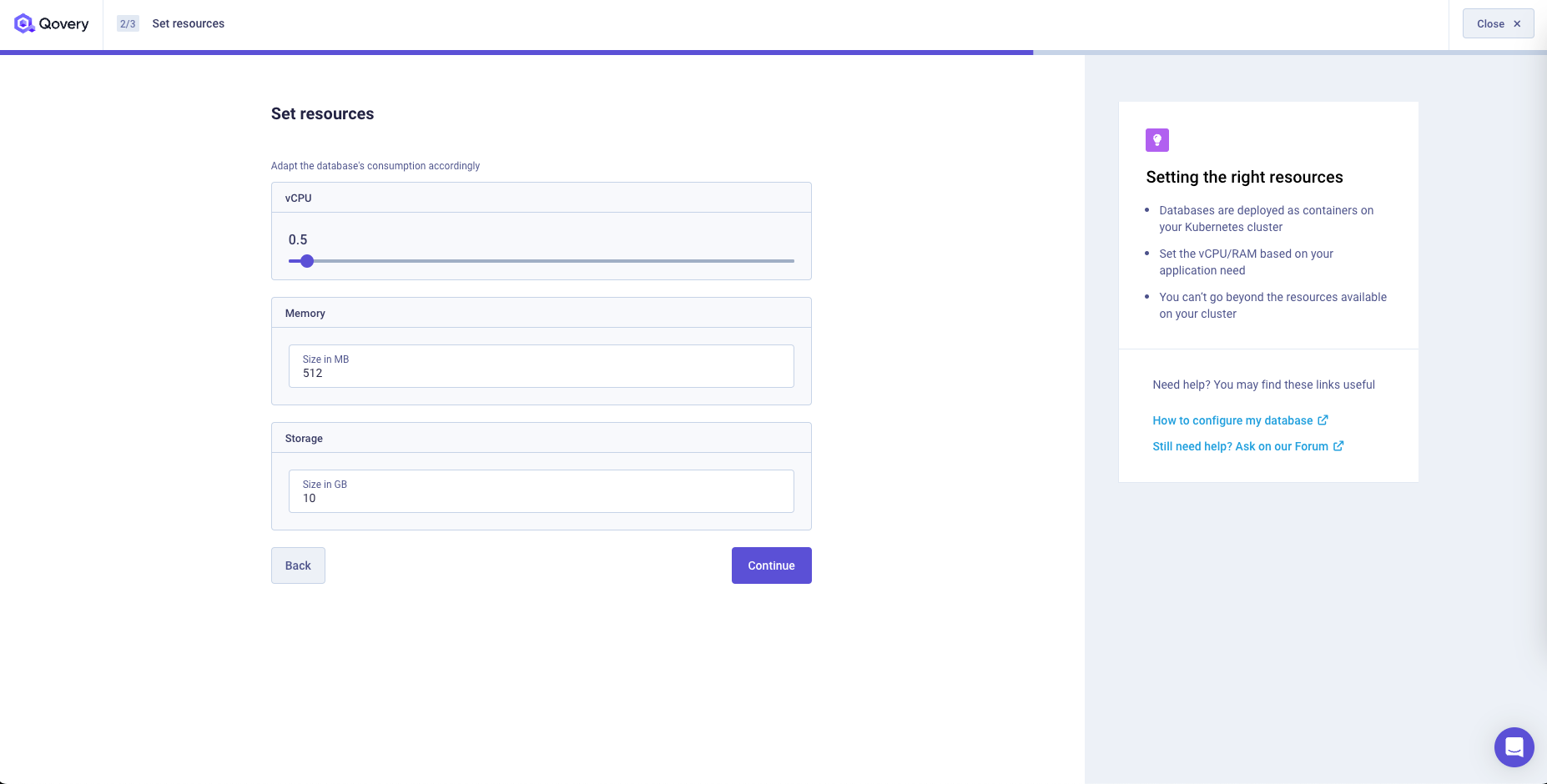
- If you are using the database in
- At the end a recap will allow you to just create the database or create and deploy it
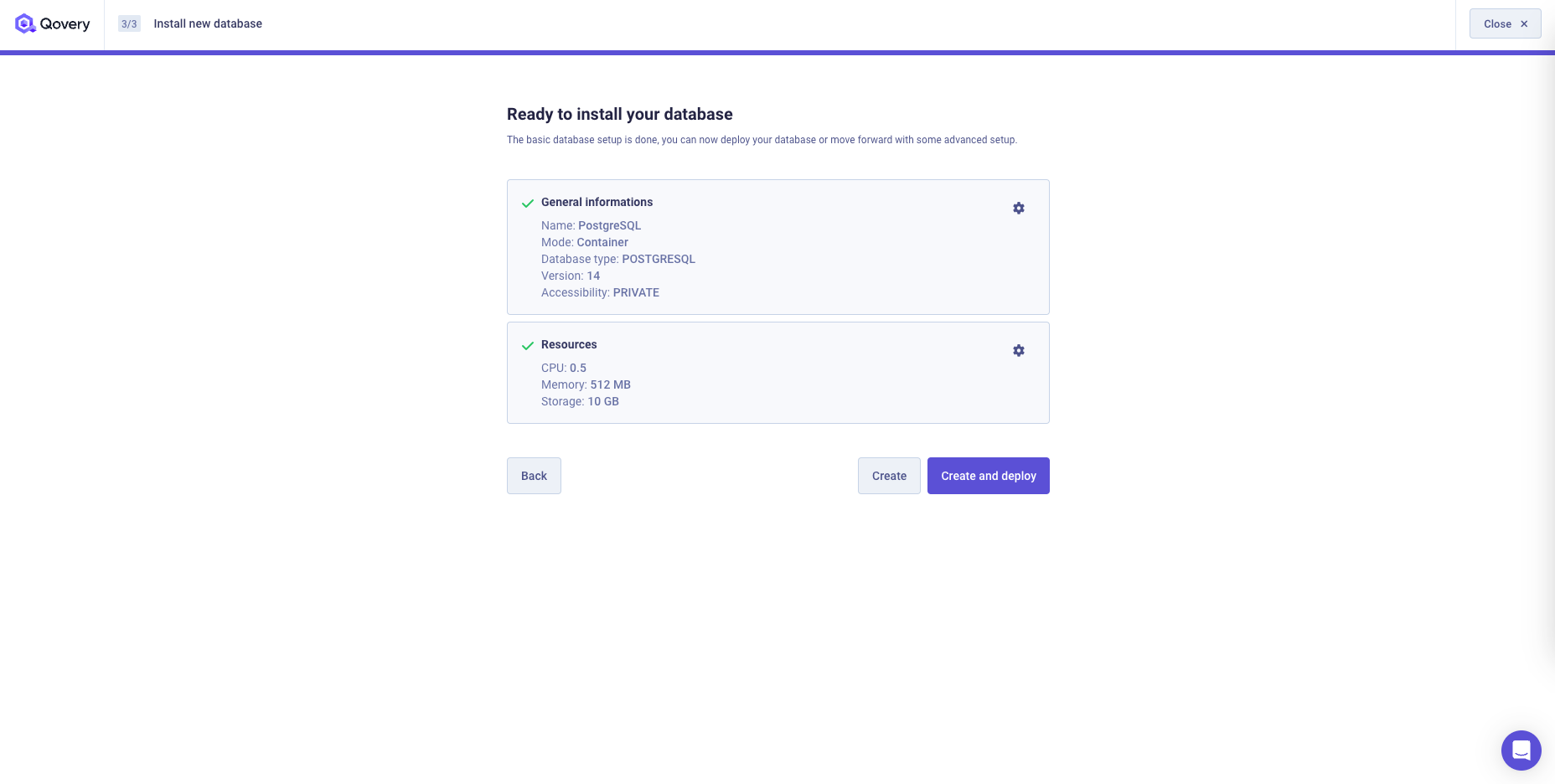
Configuration
Once created, you can access the configuration of a database at any time via the Settings tab available on the database page
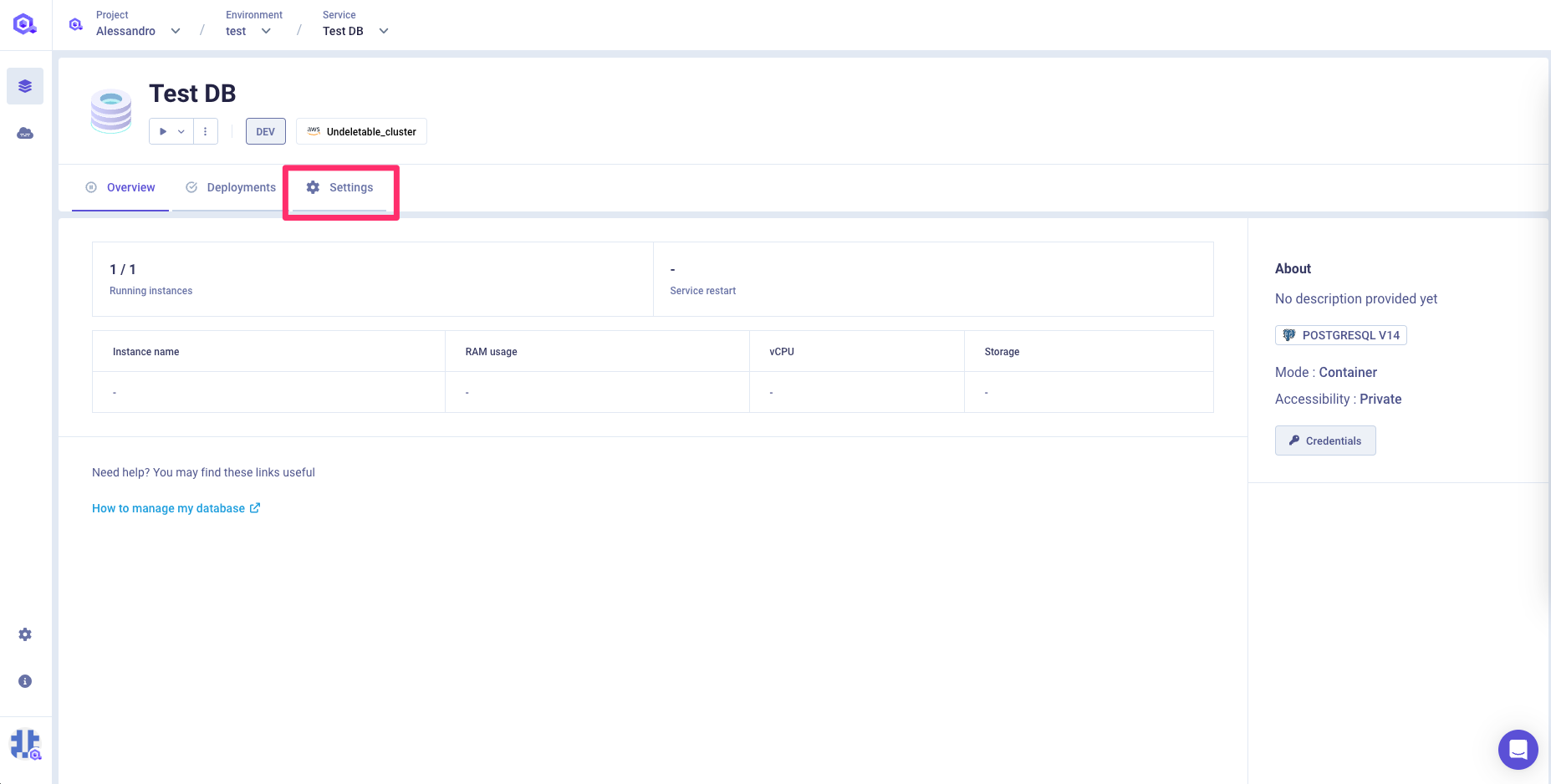
You can find below the description of each of the tabs available in this section
General
Modes
As described at the beginning of this document, databases can operate in two modes:
- Managed
- Container
Managed databases are perfect for production - they are provided and managed by major cloud providers like AWS to make sure your production data is well managed.
Container databases are managed by Qovery as Docker containers with attached persistent storage directly on your Kubernetes cluster (1 instance). They are perfect for development and testing, as they are significantly cheaper than services provided by cloud providers.
Please refer to the dedicated database sub-pages to get more information on the supported mode for each cloud provider.
Versions
We regularly update the version available for each database. Please refer to the dedicated database sub-pages to get more information on the supported version for each database types and cloud provider.
You can upgrade the version of your database directly from the Qovery interface.
Accessibility
This parameter lets you decide whether to expose publicly or not your database.
- Public access will make your database accessible via the public network
- Private access will make your database accessible only by applications in your environment
Extra labels/annotations
Add your extra annotation/label groups. See the Add annotation/label group section for more information. Annotation groups are not supported for managed databases.
Resources
CPU / Memory
This configuration is available only for databases in Container mode
You can select the CPU assigned to the Kuerbetes pod running the database instance
Instance Type
This configuration is available only for databases in Managed mode
You can modify the CPU assigned to the instance running your database (And thus, its resources).
Storage
You can select the size of the persistent storage attached to the container database.
Credentials and connectivity
When a database is created in your environment, Qovery will automatically create and inject a set of BUILT_IN environment variables containing all the parameters necessary to your application to connect to the database.
This is the list of environment variables and secrets that will be automatically created:
| Name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
QOVERY<DATABASE_TYPE><DBID>_DEFAULT_DATABASE_NAME | Env Var containing the default database name | postgres |
QOVERY<DATABASE_TYPE><DBID>_HOST | Env Var containing the external hostname of the database (if you need access from the outside and the DB is configured with visibility "PUBLIC") | zf5206c84-postgresql.oom.sh |
QOVERY<DATABASE_TYPE><DBID>_HOST_INTERNAL | Env Var containing the internal hostname of the database (if you need access it from within the cluster network) | zf5206c84-postgresql |
QOVERY<DATABASE_TYPE><DBID>_LOGIN | Env Var containing the username of the DB | superuser |
QOVERY<DATABASE_TYPE><DBID>_PORT | Env Var containing the port to be used for connecting to the DB | 5432 |
QOVERY<DATABASE_TYPE><DBID>_DATABASE_URL | Secret containing the external URI to be used for connecting to the DB (if you need access from the outside and the DB is configured with visibility "PUBLIC") | sql://root:[email protected]:27017/admin |
QOVERY<DATABASE_TYPE><DBID>_DATABASE_URL_INTERNAL | Secret containing the internal URI to be used for connecting to the DB (if you need access it from within the cluster network) | sql://root:xxxx@z4a58c1e2-postgresql:27017/admin |
QOVERY<DATABASE_TYPE><DBID>_PASSWORD | Secret containing the password of the DB | dbsecret |
Please note that the built-in variables follow the naming pattern: QOVERY_DATABASETYPE + <your_db_name> + <type_of_variable> where:
<your_db_name>is the name of your database<type_of_variable>is the type of variable we inject, e.g.PASSWORD,VERSION,CONNECTION_URIand so on.
To know how to access your database from your application, have a look at the database section.
Clone
You can create a clone of the service via the clone feature. A new service with the same configuration (see below for exceptions) will be created into the target environment.
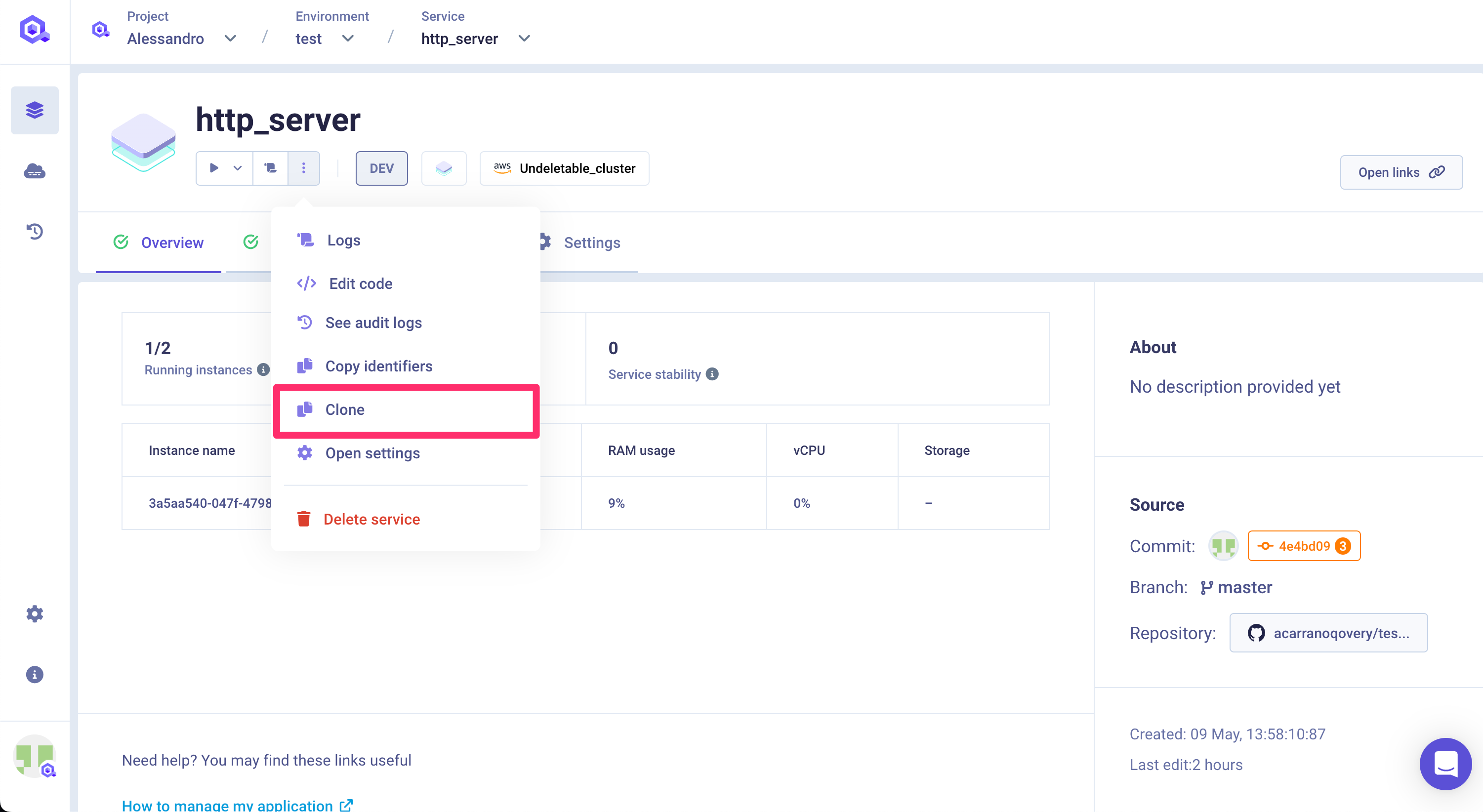
The target environment can be the same as the current environment or even another one in a completely different project.
Important information
Not every configuration parameter will be copied within the new service for consistency reasons. The configuration is fully or partially copied depending on the target environment:
- same environment:
- custom domain: this setup is not copied into the new service (to avoid collision)
- another environment:
- custom domain: this setup is not copied into the new service (to avoid collision)
- environment variable: aliases defined on environment variables are not copied (since the aliased env var might not exist)
- deployment pipeline: stage setup is not copied (since the target stage might not exist)
- number of instances: if the target environment runs on a Qovery EC2 cluster, the max number of instances is set to 1 (Qovery EC2 constraint)
Please check the configuration of the new service before deploying it.